Income Tax for Foreign Company: Tax Slabs, Forms & Deductions – 2025

Foreign companies operating in India are subject to taxation under the Income Tax Act of 1961. Understanding the income tax for foreign company is crucial to ensure compliance and know the benefits of filing ITR for foreign company. This guide covers the latest income tax rate for foreign company, the ITR form for foreign company, details regarding deductions for foreign company, and company tax slabs for FY 2026-27.
What is a Foreign Company?
As per Section 2(23A) of the Income Tax Act, a foreign company is a company that is not considered a domestic company. Any business incorporated outside India and earning income in India falls under this category.
Let’s learn more about the foreign company tax in FY 2025-26.
Foreign Company Tax Rate 2025
Income tax for domestic companies and foreign companies differs in India. The applicable foreign company tax rate in India are as follows:
| Condition | Income Tax Rate for Foreign Company |
| Royalty or Fees for Technical Services received from the Government of India or an Indian concern under an approved agreement between 1st April 1961 and 1st April 1976 | 50% |
| Any other income | 40% |
Foreign Company Income Tax Surcharge, Marginal Relief, and Health & Education Cess
- Surcharge:
- 2% if taxable income is between ₹1 crore and ₹10 crore
- 5% if taxable income exceeds ₹10 crore
- Marginal Relief: This ensures that the surcharge does not exceed the additional income beyond ₹1 crore or ₹10 crore.
- Health & Education Cess: 4% on the total foreign company tax in India (including surcharge, if applicable).
Tax Deduction for Foreign Company- FY 2025-26
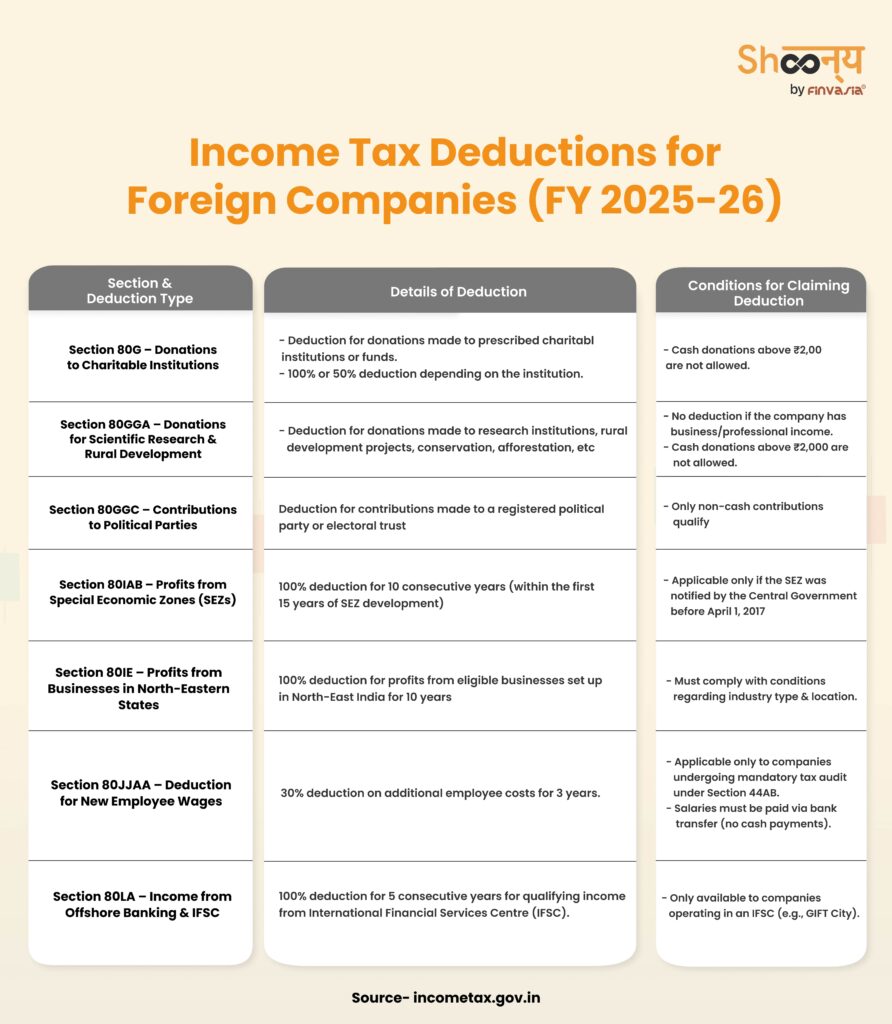
Foreign companies can benefit from deductions under Chapter VI-A of the Income Tax Act:
1. Section 80G – Donations to Charitable Funds
- Eligibility: Contributions to prescribed charitable institutions.
- Deduction Limits:
- 100% deduction for eligible donations.
- 50% deduction for certain donations.
- Condition: No cash donations above ₹2,000 allowed.
2. Section 80GGA – Donations for Scientific Research and Rural Development
- Eligibility: Contributions to approved research associations and rural development projects.
- Condition: No cash donations above ₹2,000 allowed.
3. Section 80GGC – Contributions to Political Parties
- Eligibility: Donations made to political parties or electoral trusts.
- Condition: Only non-cash contributions qualify for deduction.
4. Section 80IAB – Profits from Special Economic Zones (SEZs)
- Eligibility: Companies engaged in SEZ development.
- Deduction: 100% of profits for 10 consecutive years within the first 15 years from SEZ notification.
- Condition: No deduction if SEZ development begins after April 1, 2017.
5. Section 80IE – Profits from North-Eastern States
- Eligibility: Companies operating in North-Eastern states.
- Deduction: 100% of profits for 10 years.
6. Section 80JJAA – Deduction for New Employment
- Eligibility: Companies subject to tax audit under Section 44AB.
- Deduction: 30% of additional employee cost for three years.
7. Section 80LA – Offshore Banking Units & International Financial Services Centre (IFSC)
- Eligibility: Banking units in SEZs/IFSCs.
- Deduction: 100% of specified income for 5 consecutive years.
Tax Saving Options for Foreign Companies
Foreign companies in India can reduce their tax liability by using various tax-saving options for foreign companies, such as:
- Section 80G: Donations to eligible charitable institutions.
- Section 80IAB: Income from developing a Special Economic Zone (SEZ).
- Section 80IE: Income from businesses in the North-Eastern states.
- Section 80JJAA: Deduction for employment generation.
- Section 80LA: Income of offshore banking units.
Applicable ITR Tax Form for Foreign Company
Foreign companies operating in India must submit various forms for tax compliance. Below are key forms applicable for filing foreign income tax in AY 2025-26:
1. ITR-6
- Applicable for: Foreign companies not claiming exemption under Section 11 (Income from property held for charitable/religious purposes).
- Includes: Details of income, deductions, tax payable, and other financial information.
2. Form 26AS (Annual Information Statement – AIS)
- Provided by: Income Tax Department (Available on e-Filing Portal: Login > e-File > Income Tax Return > View Form 26AS).
- Includes:
- Tax Deducted/Collected at Source (TDS/TCS)
- Specified Financial Transactions (SFT) information
- Advance Tax payments
- Demand/Refund details
- GST and foreign government-reported information
3. Form 16A
- Issued by: Deductor to Deductee
- Purpose: Certificate of TDS on income other than salary.
- Includes:
- Amount of TDS
- Nature of payments
- TDS deposited with the Income Tax Department
4. Form 3CA-3CD
- Applicable for: Foreign companies requiring a mandatory tax audit under Section 44AB.
- Purpose: Report of audit of accounts and particulars of income.
- Due Date: One month before the due date for filing the income tax return under Section 139(1).
5. Form 3CE
- Applicable for: Non-resident taxpayers receiving royalty or technical service fees from the Government of India or an Indian concern.
- Purpose: Report from an accountant under Section 44DA, submitted one month before the tax return filing due date.
6. Form 29B
- Applicable for: Foreign companies subject to Minimum Alternate Tax (MAT) under Section 115JB.
- Purpose: Certification of book profit computation.
- Due Date: One month before the tax return filing deadline.
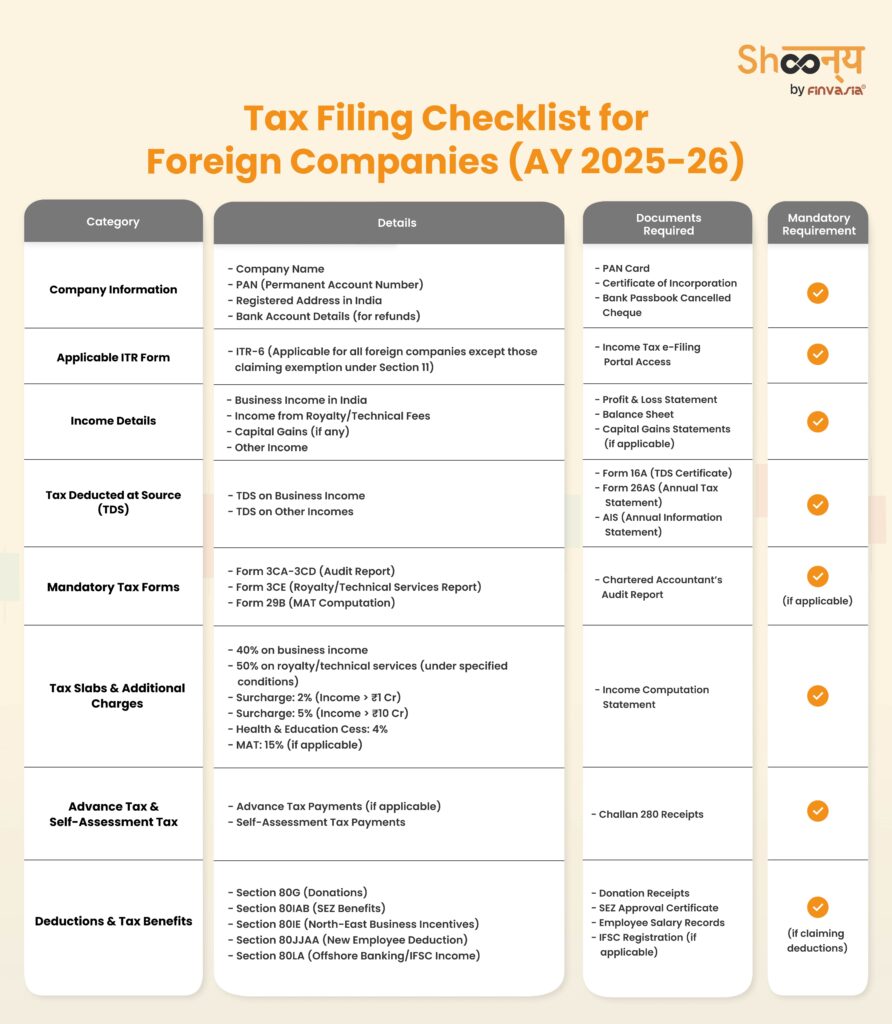
ITR Filing Checklist for Foreign Company
Before you begin filing your ITR for foreign company, you have to make sure you have all the necessary documents and details ready. Here’s a quick checklist to help you stay organised and avoid mistakes.
How to File ITR for Foreign Company
To comply with tax laws, foreign company tax filing must be done by submitting ITR-6 via the e-Filing portal of the Income Tax Department.
Step-by-Step Guide for Foreign Company Tax Filing:
- Register on the e-Filing Portal
- Visit Income Tax India e-Filing and create an account.
- Use the PAN of the foreign company to register.
- Log in and Choose the Correct ITR Form
- Select ITR-6 (for companies that do not claim exemption under Section 11).
- Pre-fill Data
- Retrieve details like TDS, foreign investments, and other foreign company income tax details from Form 26AS.
- Enter Financial Details
- Fill in all sources of income, including royalty, foreign income tax, and income tax on foreign investment.
- Claim Deductions for Foreign Companies
- Foreign companies can claim income tax deductions for foreign companies under various sections (e.g., Section 80G, 80IAB, 80IE, 80JJAA, and 80LA).
- Calculate Tax Liability
- Use the income tax calculator on the e-Filing portal to determine the foreign company tax rate.
- Pay Taxes & File the ITR
- Pay any pending taxes online and submit the return.
- E-Verify the Return
- Complete the process using Aadhaar OTP, net banking, or DSC.
Benefits of Filing ITR for Foreign Company
Filing ITR for foreign companies provides multiple advantages, including:
- Compliance & Avoiding Penalties – Filing ITR ensures compliance with Indian tax laws and helps foreign companies avoid hefty fines and legal issues.
- Tax Deductions & Savings – Foreign companies can claim deductions under various sections.
- Ease of Business Operations – Proper tax filing helps in smooth business transactions, securing regulatory approvals, and maintaining credibility.
- Avoiding Legal Complications – Timely ITR filing prevents tax disputes, audits, and restrictions on repatriating profits from India.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Tax Filing for Foreign Companies
Foreign companies operating in India must follow income tax for foreign companies regulations to avoid penalties and compliance issues. Here are some common mistakes and their consequences:
- Incorrect or Late Filing of Returns
Many foreign companies fail to file the correct ITR form for foreign companies, such as ITR-6, within the due date. Delays can result in interest charges under Section 234A and penalties under Section 234F, increasing the overall foreign company tax rate burden. Using an income tax calculator can help estimate liabilities and avoid late filings.
- Non-Compliance with TDS Requirements
Some companies do not deduct or deposit TDS on payments made to non-residents, leading to serious tax consequences. This mistake results in disallowance of expenses and additional penalties under Section 271C. As per foreign income tax laws, it is essential to deduct and deposit TDS correctly to ensure compliance.
- Failure to Obtain Required Audit Reports
Foreign companies often neglect to submit crucial audit reports like Forms 3CA-3CD, 3CE, or 29B within the deadline. This can attract a penalty of 0.5% of turnover, with a maximum limit of ₹1.5 lakh under Section 271B. Staying updated on foreign company tax filing rules can help avoid such penalties.
- Claiming Incorrect Deductions
Many foreign companies claim deductions they are not eligible for or exceed the prescribed limits. This results in additional tax liability and interest under Section 234B. Understanding income tax deductions for foreign companies ensures that only valid deductions are claimed, reducing the risk of tax demands.
- Ignoring Surcharge and Cess Calculations
Incorrect computation of surcharge and 4% health & education cess is another common mistake. Miscalculations can lead to underpayment of tax, resulting in interest and penalties under company tax in India regulations. Accurately computing tax based on foreign company tax slabs ensures compliance and prevents financial setbacks.
Conclusion
Tax compliance for foreign companies in India requires careful attention to applicable tax forms, rates, deductions, and compliance deadlines. Ensuring proper tax planning, filing correct returns, and avoiding common mistakes can help foreign businesses operate smoothly while maximising tax benefits.
Income Tax for Foreign Companies|FAQs
Yes, foreign companies earning income in India are subject to income tax. The tax rate is typically 40%, with additional surcharges and cess as applicable.
The 25% tax rate applies to certain domestic companies under Section 115BAA. Foreign companies are generally taxed at higher rates.
Domestic companies can opt for Section 115BAA to pay a reduced tax rate of 22% (plus surcharge and cess) if they forgo specific exemptions and deductions.
Foreign companies are taxed at 40% on their total income, with a 50% tax on royalties and technical service fees under specified agreements.
The 2025 tax changes include revised slabs, surcharge rates, and deductions. Check the latest Income Tax Act amendments for exact details.
Yes, TDS is deducted on payments made to foreign companies for services like royalties, technical fees, and dividends, as per the applicable tax treaties.
Yes, if you are a resident of India, salary from a foreign company is taxable in India. Non-residents are taxed only on income earned in India.
TCS on foreign remittances can be avoided by providing valid documentation, such as proof of education expenses or tax residency certificates.
Domestic companies pay 22-30% tax under different schemes, while foreign companies are taxed at 40%, plus surcharges and cess.
The corporate tax rate depends on company type; domestic companies pay between 22%-30%, whereas foreign companies pay 40%, plus applicable surcharges.
Foreign companies are taxed at 40% on general income and 50% on specific royalties or fees for technical services under certain agreements.
Source- Incometax.gov.in
______________________________________________________________________________________
Disclaimer: Investments in the securities market are subject to market risks; read all the related documents carefully before investing.








