Bull vs Bear: Understanding Market Dynamics

You’ve probably come across the terms “bull” vs “bear” markets when talking about the stock market. But what do they really mean? These aren’t just animals—they represent two very different market conditions. Knowing the difference between bull and bear market is key to planning bull market strategies and bear market strategies. But what exactly is a bull vs. bear market?
This is what we will learn today!
Let’s begin.
Where Do the Terms “Bull” and “Bear” Come From?
The terms “bull” and “bear” come from the way these animals behave. Bulls charge forward, symbolizing a market that’s surging. Bears, on the other hand, hibernate or withdraw, which represents a market that’s pulling back.
Bull vs. Bear Markets: Understanding the Origins
The origins of these terms lie in their associated animal behaviours. A bull, charging ahead with its horns raised, symbolises an advancing market. Conversely, a bear, with its clawed grasp, represents a market dragging downwards.
This metaphor underscores the market’s dynamics: ascending as it charges ahead and descending as it’s pulled down.
What is Bull Market?
A bull market is a financial market where prices rise over time. It is often marked by a 20% increase from recent lows. This period reflects investor confidence and optimism. It is supported by strong economic indicators like low unemployment and high GDP growth. Bull markets can happen in different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities.
In simple terms, a bull market happens when the stock market is going up. This is usually accompanied by the good condition of the economy. Prices of stocks keep rising, and people feel positive about the future. During a bull market, the economy is usually strong.
Some common indicators of Bull Market
Here are some common signs of a bull market:
- Stock prices increase by 20% or more from recent lows.
- Investors are optimistic and buy more stocks.
- Low unemployment, high GDP growth, and strong consumer spending.
- Companies show higher earnings and revenue growth.
- Central banks keep interest rates low to boost economic growth.
- More investors are actively buying and selling stocks.
Bull Market Strategy
In a bull market, prices are rising and investor confidence is high.
Here’s how to make the most of this positive trend:
- Buy and Hold: You must invest long-term to benefit from rising prices.
- Focus on Growth Stocks: It is a better idea to invest in companies with strong growth potential and good financial health.
- Diversify Investments: Portfolio diversification is indeed a perfect bearish vs bullish strategy.
- Take Profits and Reinvest: You must regularly update your portfolio. Reinvesting your income in new opportunities is always a good idea.
- Monitor Market Conditions: As a responsible trader, you must use market technical indicators. They can help you track trends and adjust your strategy as needed.
What is Bear Market?
It is a financial market where prices fall significantly, typically by 20% or more from recent highs. It often comes with widespread investor pessimism and a weakening economy. Bear markets can impact individual stocks, commodities, or broad market indices.
A notable example from India’s history is the 2008 financial crisis. Smart investors bought good stocks at lower prices during the downturn. Those who kept their investments saw significant profits when the market eventually bounced back.
People tend to feel more cautious or negative about the market’s future during these times.
What are some common bear market indicators?
- A decline of 20% or more in major stock indices over at least two months.
- Rising unemployment rates. This would indicate an economic slowdown.
- Falling corporate earnings and revenue growth.
- An increased stock market volatility and market fear. This is often measured by the VIX index.
- A trend of decreasing consumer confidence and spending.
Bear Market Strategy
In a bear market, prices are falling, and the market feels uncertain.
Here’s how to trade cautiously:
- Portfolio Diversification: You must spread your investments across different industries and asset classes to lower risk.
- Invest in Defensive Stocks: You can focus on sectors like utilities, healthcare, and consumer essentials that are less affected by downturns.
- Hold Cash or Bonds: It is better to increase your holdings in cash or government bonds to protect your money.
- Consider Inverse ETFs: These funds go up in value when the market falls. This can help you hedge against losses.
Before we jump to understand the stock market bull vs bear, let us understand the concept of bull market.
Bull Market vs Bear Market: A Comprehensive Overview
A bull market signifies a market that is ascending, accompanied by a robust economy. Conversely, a bear market prevails when the economy is contracting, leading to a decline in most stocks’ value. These terms, “bull” and “bear,” also reflect how investors feel—optimistic in a bull market and pessimistic in a bear market.
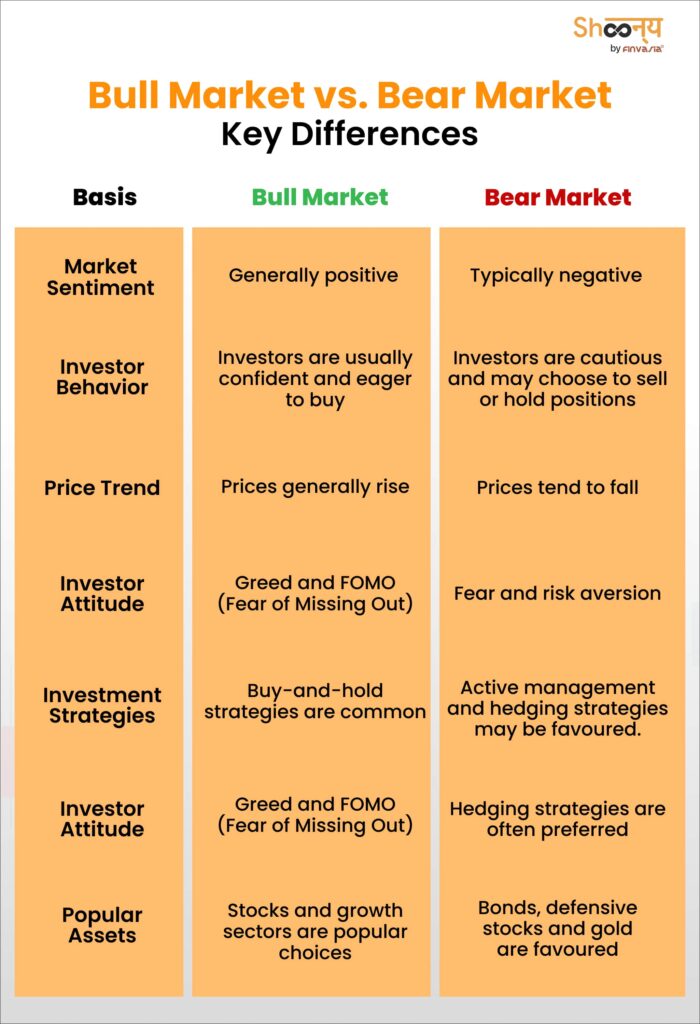
Economic Conditions
Let’s talk about how the stock market and the economy are connected.
When the economy is doing well—high GDP growth, low unemployment, etc.—stock markets usually rise, which we call a bull market. But when the economy slows down, with GDP dropping and unemployment rising, stock markets tend to fall. This leads to a bear market.
Investment Strategies
In a bull market, where prices are rising, you might want to focus on growth stocks and long-term investments. But when things turn bearish, and prices drop, it’s often safer to look at defensive stocks, bonds, or assets that don’t follow the market trends as closely.
The key is to stay calm and avoid emotional decisions.
Investor Psychology
How we feel about the market can really influence what happens.
When people are optimistic during a bull market, they tend to buy more, pushing prices up even further.
But in a bear market, fear and anxiety often lead to selling, which drives prices down.
If you can understand these emotional reactions, like herd mentality and overconfidence, you can avoid common stock market mistakes!
Market Timing
Trying to time the market—predicting when prices will go up or down to buy or sell at the right time—can be really tough. Markets are unpredictable, and even the best analysis can’t always get it right.
That’s why a long-term investment approach is often safer!
Supply and Demand for Securities
The basic idea of supply and demand also applies to stocks.
In a bull market, when everyone wants to buy, and there aren’t many sellers, prices go up. In a bear market, the opposite happens—more sellers than buyers push prices down.
Knowing this can help you make better decisions about when to enter or exit the market.
Dollar-Cost Averaging
One smart way to invest is through dollar-cost averaging. This means putting in a fixed amount of money at regular intervals.
By doing this, you buy more shares when prices are low and fewer when they’re high. It is bound to help you build wealth steadily over time.
What to Do in Each Market| Stock Market Bull vs Bear
In a Bull Market: When the stock market is rising (bull market), it’s a good idea to buy stocks early in the trend. As prices continue to go up, you can potentially sell them later at a higher price. During a bull market, losses are usually small and short-lived. Thus, you can invest more.
In a Bear Market: In a bear market, where prices are falling, the risk of losses is higher. Investing during this time can be tricky. This is because prices may keep dropping, and it’s hard to predict when they’ll stop. Instead of buying stocks, some investors might look at safer options like fixed-income securities. However, some others consider short selling, which allows you to profit from falling prices.
Conclusion
Navigating bull and bear markets requires a deep understanding of their dynamics. By recognising the nuances, you can develop informed strategies tailored to the market’s ebb and flow. Remember, successful investing hinges on a blend of knowledge, strategy, and a careful assessment of market sentiment.
FAQs| Bull vs Bear
Bull markets are generally preferred because they indicate rising prices and economic growth.
The names come from how the animals attack: bulls thrust upward with their horns, while bears swipe downward with their paws.
A market is bullish if prices are consistently rising and bearish if prices are consistently falling.
Bullish usually means buy, as it indicates an expectation that prices will rise.
The bull/bear ratio is a market sentiment indicator comparing the number of bullish to bearish advisors.
A bull run is marked by sustained upward price movements, higher trading volumes, and positive market sentiment.
A bull or bear phase arises from economic factors. These phases alternate over time. Bull markets tend to be longer and more prevalent than bear markets.
Monitor price movements over time. A bull market entails sustained upward movement, while a bear market involves a continuous decline.
Source: Investopedia
______________________________________________________________________________________
Disclaimer: Investments in the securities market are subject to market risks; read all the related documents carefully before investing.








