Income Tax for Firm/LLP in India: Comprehensive Guide with Latest Budget 2025 Updates

Getting a grip on the complexities of Income Tax for Firm/LLP is crucial for effective financial management and compliance in India. While both partnership firms and LLPs are distinct legal entities with their own liabilities as outlined in the Income Tax Act of 1961, this guide takes a deep dive into the taxation landscape for these entities. It includes the latest updates from the Union Budget 2025 and offers valuable insights into Income Tax for Firm/LLP, including tax slabs, deductions, filing procedures, and much more.
What is Income Tax for Firm/LLP?
In the context of firms and LLPs, income tax pertains to the tax imposed on the income of profit earned Indian partnership firms and Limited Liability Partnership. Such Persons are the legally independent bodies and as such their partners, are separate and distinct for the purposes of income tax and have separate rates and provisions as per the Income Tax Act, 1961.
What is an LLP?
A Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) is a business structure that is very popular in India because it takes the benefits of a partnership firm and a company. As per the Limited Liability Partnership Act of 2008, an LLP enjoys autonomy in operations along with limited liability protection for partners which means their personal assets are protected in the event of business losses. An LLP needs a minimum of two partners for incorporation, but there is no cap on the maximum number of partners. Out of them, minimum two have to be designated partners, one of whom has to be an Indian resident. The LLP in turn complies with the LLP agreement by assigning roles, rights, and responsibilities to its partners and the LLP Act, 2008 in return provides legal validity and operational transparency to the firm. LLPs have many features such as perpetual succession which means that the LLP will remain in existence regardless of changes in partners making it a more suitable option for entrepreneurs in need of a flexible structured business entity.
What is a Partnership Firm?
In India, a partnership firm is one of the oldest business structures, and it is highly preferred because of its easy setup. This structure is established when two or more people join together, contribute resources, and sign a partnership contract to conduct a business under a common firm name. The partnership agreement outlines how each partner will contribute to the company, and divides profits among partners, and allocates roles and responsibilities to every individual in the partnership. The registration of companies with limited liability, for example, makes it impossible for a firm to operate in a registered name, Therefore, a partnership firm can still operate without being legally registered. Unfortunately, all partners in a partnership lose the protection of limited liability as they become personally liable to repay any debts or losses that the firm incurs. Because of the uncomplicated nature of setting up a partnership firm, it is the choice for many family businesses and small companies in India.
Latest Updates for the AY 2025-26: Income Tax for Firm/LLP
For the Assessment Year (AY) 2025-26, income tax for LLP and Partnership Firms in India is subject to a flat income tax rate of 30% on their total income. This income tax rate for firm entities remains consistent regardless of income levels. However, in addition to this base tax rate, LLPs may also be liable to pay other charges, including surcharge, marginal relief, and health & education cess, depending on their taxable income. These additional charges can impact the overall tax liability of an LLP, making it essential for businesses to understand how they are calculated. Let’s break them down in detail:
What is Surcharge?
A surcharge is an extra tax levied on top of the regular income tax if a firm’s taxable income crosses ₹1 crore. The surcharge rates are as follows:
- 12% of the income tax amount if the taxable income exceeds ₹1 crore.
What is Marginal Relief?
To prevent an excessive tax burden due to the surcharge, the marginal relief rule applies. Here’s how it works:
- If the firm’s net income exceeds ₹1 crore, the total tax payable (including surcharge) should not be higher than the tax on ₹1 crore by more than the excess income over ₹1 crore.
- This ensures that firms don’t pay disproportionately high taxes just because their income slightly exceeds the threshold.
What is Health & Education Cess?
In addition to the income tax and surcharge, firms and LLPs must also pay a Health & Education Cess of 4% on the total tax amount, including surcharge (if applicable). This cess helps fund educational and healthcare initiatives across India.
Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) for LLPs & Firms
LLPs and firms must also be aware of Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT). If their normal tax liability is less than 18.5% of their book profit, they must pay AMT at 18.5% of book profit (plus surcharge and cess, if applicable).
In summary, while LLPs and firms are taxed at a flat 30% rate, the partnership firm tax rate also follows the same structure. However, additional charges like surcharge, marginal relief, and AMT play a role in determining the final tax outgo. Understanding these components can help firms plan their finances and tax-saving strategies efficiently!
Firm/LLP Tax Slabs for AY 2025-26: Old Tax Regime vs. New Tax Regime
For partnership firms and LLPs, the tax structure is straightforward, with a flat LLP taxation rate applicable irrespective of income levels.
Old Tax Regime:
- Tax Rate: 30% on total income.
- Surcharge: 12% if income exceeds ₹1 crore.
- Health and Education Cess: 4% on income tax and surcharge.
New Tax Regime:
- The new tax regime introduced for individuals and HUFs does not impact the taxation of partnership firms and LLPs. These entities continue to be taxed at the flat rate under the old regime.
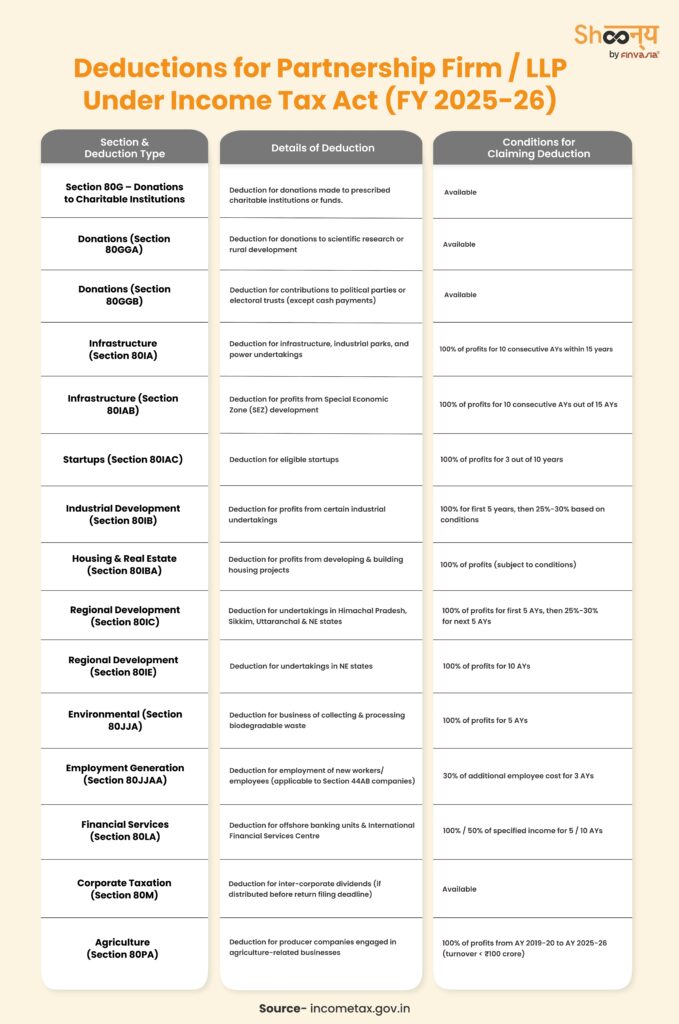
Income Tax Deductions for Firm/LLP (FY 2025-26)
Just like individuals and HUFs, Firms and LLPs can also take advantage of various deductions under the Income Tax Act to optimize their tax liability. Since a Firm or LLP is treated as a separate legal entity for tax purposes, it can claim deductions independently, regardless of the income earned by its partners. By strategically utilizing these deductions, Firms and LLPs can significantly reduce their taxable income, ensuring better financial planning and compliance. The following table outlines key deductions available to Firms and LLPs that can help in tax-saving and efficient business management:
ITR Forms for Firm/LLP for AY 2025-26
Firms and LLPs must file their income tax returns using the appropriate forms. Here’s a quick overview of the applicable returns:
1. ITR-4 (Sugam) – For Firms (Except LLPs)
Applicable for resident Firms (other than LLPs) with total income up to ₹50 lakh, filing under the presumptive taxation scheme (u/s 44AD, 44ADA, or 44AE). It covers:
- Income from Business/Profession (presumptive taxation)
- One House Property
- Other income (interest, pension, dividends, etc.)
- Agricultural income up to ₹5,000
Not eligible if:
- Director in a company
- Holds unlisted equity shares
- Has foreign assets/income
- Has total income exceeding ₹50 lakh
Note: ITR-4 is optional and can be used at the assessee’s discretion.
2. ITR-5 – For LLPs & Other Entities
Applicable for:
- LLPs, Firms, AOPs, BOIs, Cooperative Societies, Trusts, Estates, and Business Trusts.
Not for:
- Entities required to file ITR under sections 139(4A), 139(4B), or 139(4D).
Remember, filing the right ITR ensures compliance and smooth tax processing!
Important Income Tax Forms for AY 2025-26
Here’s a quick guide to key tax forms and their purposes:
Key Income Tax Forms for AY 2025-26
| Form | Submitted/Provided By | Purpose & Details |
| Form 26AS & AIS | Income Tax Department | Provides details of TDS/TCS, tax payments, refunds, SFT transactions, GST info, and foreign government data. Available on e-Filing Portal. |
| Form 16A | Deductor to Deductee | Quarterly TDS certificate for non-salary income, showing TDS amount, nature of payments, and tax deposited. |
| Form 3CA-3CD | Taxpayer requiring audit under any other law | Mandatory audit report under Section 44AB. Must be filed 1 month before the ITR due date. |
| Form 3CB-3CD | Taxpayer undergoing audit under Section 44AB | Audit report and financial particulars. Required 1 month before the ITR deadline. |
| Form 3CEB | Taxpayer with international or specified domestic transactions | Report by a chartered accountant on transfer pricing transactions under Section 92E. |
| Form 3CE | Non-resident taxpayers/foreign companies earning royalty or fees in India | Accountant report for income under Section 44DA. |
| Form 29C | Taxpayer subject to Alternate Minimum Tax (AMT) | Report for computing Adjusted Total Income & AMT under Section 115JC. |
| Form 67 | Taxpayer claiming Foreign Tax Credit | Statement of foreign income & tax paid, to be submitted before the ITR due date. |
| Form 10CCB | Taxpayer claiming deductions under Sections 80-I, 80-IA, 80-IB, 80-IC, or 80-IE | Mandatory audit report to claim tax deductions, filed 1 month before the ITR due date. |
Filing the right forms ensures smooth tax compliance and maximizes tax benefits!
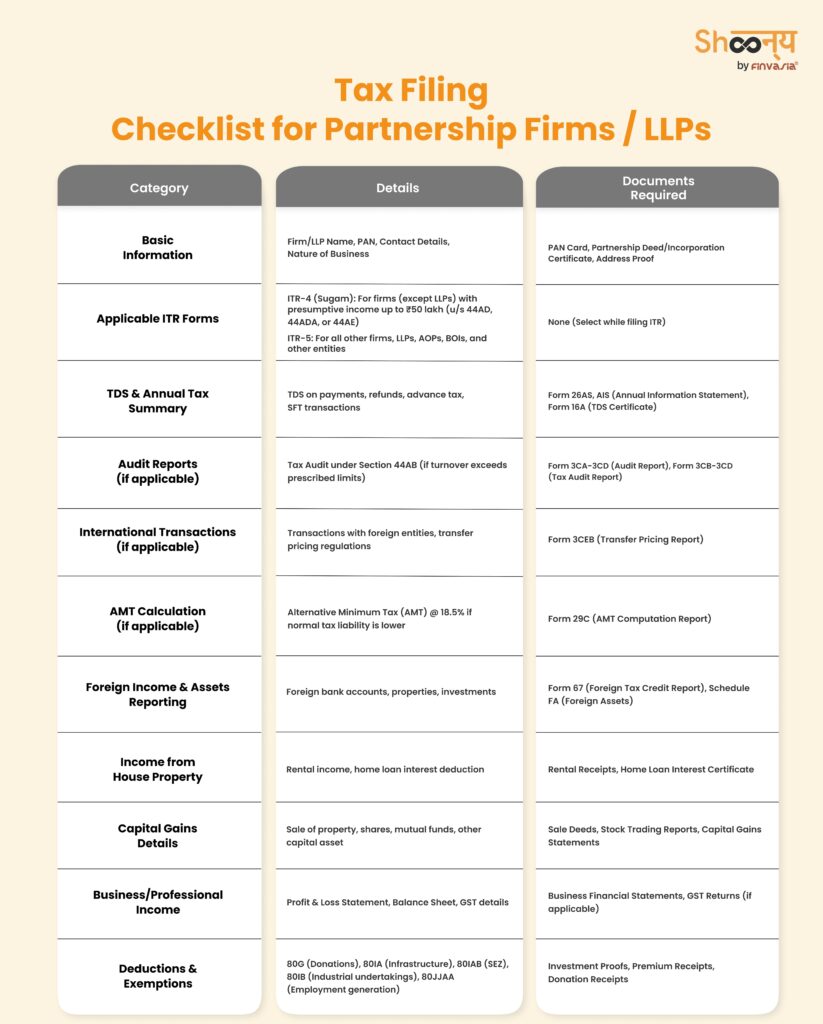
Checklist for Firm/LLP ITR Filing
Before filing income tax returns, firms and LLPs should ensure they have the following documents and details ready:
How to File ITR for Firm/LLP
Firms (excluding LLPs) can file ITR-4 online via the e-Filing portal or using offline utilities. This guide outlines the online filing process.
1. Log in & Start Filing
- Go to the e-Filing portal, log in with PAN & password.
- Navigate to e-File > Income Tax Returns > File ITR.
- Select AY 2024-25, choose Online Mode, and proceed.
2. Select ITR & Filing Status
- Choose ITR-4 from the dropdown.
- Review and confirm pre-filled personal details.
3. Enter Income Details
- Verify income sources (Salary, Business, Other).
- Add financial disclosures & exempt income details.
4. Claim Deductions
- If opting for Old Tax Regime, provide deductions under Chapter VI-A.
- If claiming 80DD or 80U, file Form 10-IA first.
5. Verify Taxes Paid & Tax Liability
- Confirm TDS, TCS, Advance Tax & Self-Assessment Tax.
- Check total tax liability/refund.
6. Pay Tax (if applicable)
- Choose “Pay Now” for instant tax payment.
- If opting for “Pay Later,” ensure timely payment to avoid interest.
7. Preview & Submit
- Click Preview Return, verify details & submit.
8. E-Verify Your ITR
- Recommended: e-Verify immediately using Aadhaar OTP, Net Banking, or DSC.
- Alternatively, send signed ITR-V to CPC Bengaluru within 30 days.
*Important Notes
- New Tax Regime is Default – Opt out via Form 10-IEA before filing if choosing Old Regime.
- PAN-Aadhaar Link Mandatory – Inoperative PANs will have limited portal access.
- E-Verification is Required – Must be done within 30 days, else late fees may apply.
By following these steps, you can successfully file your ITR-4 for your Firm/LLP with ease.
Step-by-Step Guide to Income Tax Filing for LLP
1. Maintain Proper Books of Accounts
Before filing ITR, LLPs must maintain accurate financial records of:
- Income & expenses
- Assets & liabilities
- Profit & Loss statements
- Balance sheets
2. Determine Whether a Tax Audit is Required
LLPs must undergo a tax audit if:
- Turnover exceeds ₹40 lakh OR
- Contribution exceeds ₹25 lakh
New Rule: If an LLP’s turnover is under ₹5 crore and cash transactions are less than 5%, it may be exempt from tax audits.
ITR Filing Deadlines:
- Without tax audit: July 31
- With tax audit: September 30
3. Choose the Correct ITR Form (ITR-5)
LLPs must file their returns using Form ITR-5, which includes:
- Income details
- Tax liability computation
- Business & financial information
4. Filing Process for ITR-5
Step 1: Login to the Income Tax e-Filing Portal using your LLP’s credentials.
Step 2: Select Form ITR-5 and fill in financial details.
Step 3: Verify tax liability and claim deductions (if applicable).
Step 4: E-verify using Digital Signature Certificate (DSC).
Step 5: Submit and download the acknowledgment for records.
5. Additional Compliance Requirements for LLPs
Apart from ITR filing, LLPs must also comply with annual MCA and tax regulations:
| Form | Purpose | Due Date | Penalty for Late Filing |
| Form 11 | Annual Return Filing | May 30 | ₹100/day |
| Form 8 | Statement of Accounts & Solvency | October 30 | ₹100/day |
| ITR-5 | Income Tax Return (No Tax Audit) | July 31 | Late fee up to ₹5,000 |
| ITR-5 | Income Tax Return (With Tax Audit) | September 30 | Late fee up to ₹5,000 |
| Form 3CEB | International Transactions Reporting | November 30 | Varies |
Note: Non-compliance can result in hefty penalties, legal consequences, and operational restrictions.
Common Mistakes to Avoid While Filing ITR for Firm/LLP
1. Choosing the Wrong ITR Form – LLPs and firms must file ITR-4 or ITR-5.
2. Not Conducting a Tax Audit – If turnover exceeds the specified limit, tax audit under Section 44AB is mandatory.
3. Incorrect Computation of Partner Remuneration – Exceeding allowable limits can lead to disallowances.
4. Not Reconciling with Form 26AS – Mismatches can result in tax notices.
5. Late Filing – Attracts penalties under Section 234F.
Assisted ITR Filing for Firm/LLP: A Smarter Approach
Filing Income Tax Returns (ITR) for Firms and LLPs can be complex, involving multiple legal and financial considerations. Businesses can streamline the process by opting for professional tax filing services, which provide:
1. Expert Guidance & Tax Optimization Strategies
- Professionals analyze financial statements to identify eligible deductions and optimize tax liabilities.
- Assistance in structuring expenses and investments for better tax efficiency.
- Strategic tax planning ensures firms and LLPs take full advantage of rebates and exemptions under the Income Tax Act.
2. Ensuring Full Compliance with Legal Provisions
- LLPs and firms must comply with income tax laws, MCA regulations, and GST requirements.
- Experts help ensure timely filing of Form ITR-5, Form 11, Form 8, and any additional regulatory filings.
- Prevents issues like missed deadlines, incorrect filings, or incomplete documentation that may lead to notices or penalties.
3. Avoiding Costly Errors & Penalties
- Incorrect reporting of income, expenses, or deductions can trigger tax scrutiny and legal complications.
- Late filing penalties can go up to ₹5,000 under Section 234F, apart from daily penalties for MCA filings.
- Professionals ensure error-free submissions, reducing compliance risks.
4. Audit & Documentation Support
- LLPs with a turnover above ₹40 lakh or contributions exceeding ₹25 lakh require tax audits under the Income Tax Act.
- Assistance with maintaining proper financial records, tax reports, and audit documentation for regulatory scrutiny.
- Firms engaging in international transactions get support in filing Form 3CEB for transfer pricing compliance.
Income Tax Calculator: How to Use It?
An income tax calculator is a valuable tool that helps firms and LLPs estimate tax liability based on various factors. These tools help businesses plan finances effectively, avoiding last-minute surprises.
Key Components of an Income Tax Calculator
1️. Gross Total Income – Includes business profits, interest income, rental income, and any other earnings.
2. Deductions & Exemptions – Computes benefits under Sections 80C, 80D, 80G, and other applicable provisions.
3. Surcharge & Cess – Calculates additional tax based on income slabs. LLPs with income above ₹1 crore attract a 12% surcharge.
4. Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) for LLPs – LLPs must pay 18.5% AMT if tax under normal provisions is lower. The calculator factors this in.
Where to Access Tax Calculators?
1. Income Tax Department’s Official Website – Free government-provided tax calculation tool.
2. Bank & Financial Portals – Private platforms offer tax estimation tools with added insights.
3. CA/Tax Professional Software – Advanced software helps businesses with accurate tax planning.
Benefits of Filing ITR for Firms & LLPs
1. Legal Compliance & Good Standing
- Timely tax filing ensures compliance with Income Tax Act, 1961, and LLP Act, 2008.
- Helps businesses avoid penalties, legal notices, or disqualification from government tenders.
2. Smooth Loan & Credit Approvals
- Banks and NBFCs require ITR receipts of the last 3 years for business loan approvals.
- Filing ITR enhances financial credibility and increases loan eligibility.
3. Faster Tax Refund Processing
- LLPs eligible for tax refunds due to TDS deductions or excess tax payments can claim refunds faster with timely filing.
- Delayed filings may result in prolonged verification and refund processing times.
4. Lower Chances of Tax Scrutiny
- Non-filing or underreporting income can trigger scrutiny from the Income Tax Department.
- Proper tax filing minimizes the risk of tax assessments, audits, and inquiries.
Conclusion
Filing ITR for Firms & LLPs is essential for financial stability, regulatory compliance, and tax optimization. The latest Budget 2025 updates have reaffirmed existing tax structures while introducing measures to ease compliance for businesses. By understanding tax slabs, deductions, AMT provisions, and compliance deadlines, businesses can effectively manage their tax liabilities. Seeking professional tax assistance ensures error-free filing, audit readiness, and hassle-free compliance.
Stay compliant, optimize your tax burden, and ensure financial success by filing your LLP’s ITR on time!
Income Tax for Firm/LLP | FAQs
The LLP tax rate is 30% of total income. Additionally, surcharge (12%) and cess (4%) apply if total income exceeds ₹1 crore.
LLPs must file ITR-5 online through the Income Tax e-Filing portal, with mandatory DSC verification for submission.
There are no slabs for LLPs and firms—they are taxed at a flat 30% rate.
Yes, if turnover exceeds ₹1 crore, tax audit under Section 44AB is mandatory.
The due date is July 31 for non-audited accounts and October 31 for audited accounts.
No, LLPs cannot claim deductions under Section 80C, but they can avail deductions under Section 35AD, 80JJAA, and 80-IA/IB.
A late filing penalty of up to ₹10,000 applies, along with interest under Section 234A on tax due.
Source- Incometax.gov.in
______________________________________________________________________________________
Disclaimer: Investments in the securities market are subject to market risks; read all the related documents carefully before investing.








