Portfolio in Stock Market: Value, Income or Growth, Which One is Better?

You may have heard the term “portfolio” many times. But what exactly is a portfolio, and why is it so important for investors? How can you create and manage your own portfolio in the stock market to achieve your financial goals?
In this blog post, we will answer these questions as we explore the concept of portfolio in the stock market.
Portfolio Meaning in Stock Market
A portfolio in the stock market is a collection of financial assets that an investor owns and trades in the market.
In the stock market, your “portfolio” is like a collection of investments you own.
It’s not just one stock but a bunch of them, like pieces of a puzzle.
Each piece (or stock) can be from different companies or sectors.
Your portfolio’s goal is to make you money over time by growing in value.
So, when people talk about their portfolio in the stock market, they’re basically talking about all the assets they’ve invested in.
These assets can include stocks, bonds, mutual funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), etc.
For example, when you step into stock market trading, may own shares of Infosys, Reliance, HDFC Bank, and Tata Motors.
These will all together represent your portfolio in the stock market.
The main purpose of having a portfolio is to diversify your investments, reduce your risk, and increase your returns.
By investing in different types of assets, you can spread your money across various sectors, industries, and markets.
This way, you can reduce the impact of market fluctuations and volatility on your portfolio and benefit from the growth potential of different assets.
Types of Portfolio in the Stock Market
There are different types of portfolios in the stock market. Each type suits different needs, allowing investors to tailor their choices.
Some of the common types of portfolios are:
Income Portfolio
This type of portfolio focuses on generating regular income from the investments rather than capital appreciation.
Income-oriented investors seek investments that generate regular income. They may opt for high-dividend stocks, fixed-interest bonds, or income-distributing mutual funds.
An income portfolio is suitable for investors who need a steady source of cash flow, such as retirees or conservative investors.
Growth Portfolio
This type of portfolio aims to maximise the capital appreciation of the investments rather than income.
For example, if you are a growth-oriented investor, you may invest in stocks that have high growth potential.
You can explore emerging top companies, innovative technologies, or disruptive business models.
A growth portfolio is suitable for investors who are willing to take more risk, and have a long-term investment horizon, such as young investors or aggressive investors.
Value Portfolio
This type of portfolio seeks to invest in undervalued assets, that is, assets that are trading below their intrinsic value.
For example, if you are a value-oriented investor, you may invest in stocks that have low price-to-earnings (P/E), price-to-book (P/B), or price-to-cash flow (P/CF) ratios compared to their peers or the market average.
A value portfolio is suitable for investors who are looking for bargain deals. Or, fr someone with a medium to long-term investment horizon.
Growth and Value Portfolio
This type of portfolio combines the elements of both growth and value investing.
Do you belong to the category that wishes for a flexible investment horizon?
This can be for you!
It invests in both undervalued and high-growth assets.
For example, a growth and value-oriented investor may invest in stocks that have low valuations but also have strong earnings and revenue growth.
A growth and value portfolio is suitable for investors who want to balance risk and return.
Value Portfolio vs Growth Portfolio
Are you also confused about choosing one between a value portfolio and a growth portfolio?
Check this out.
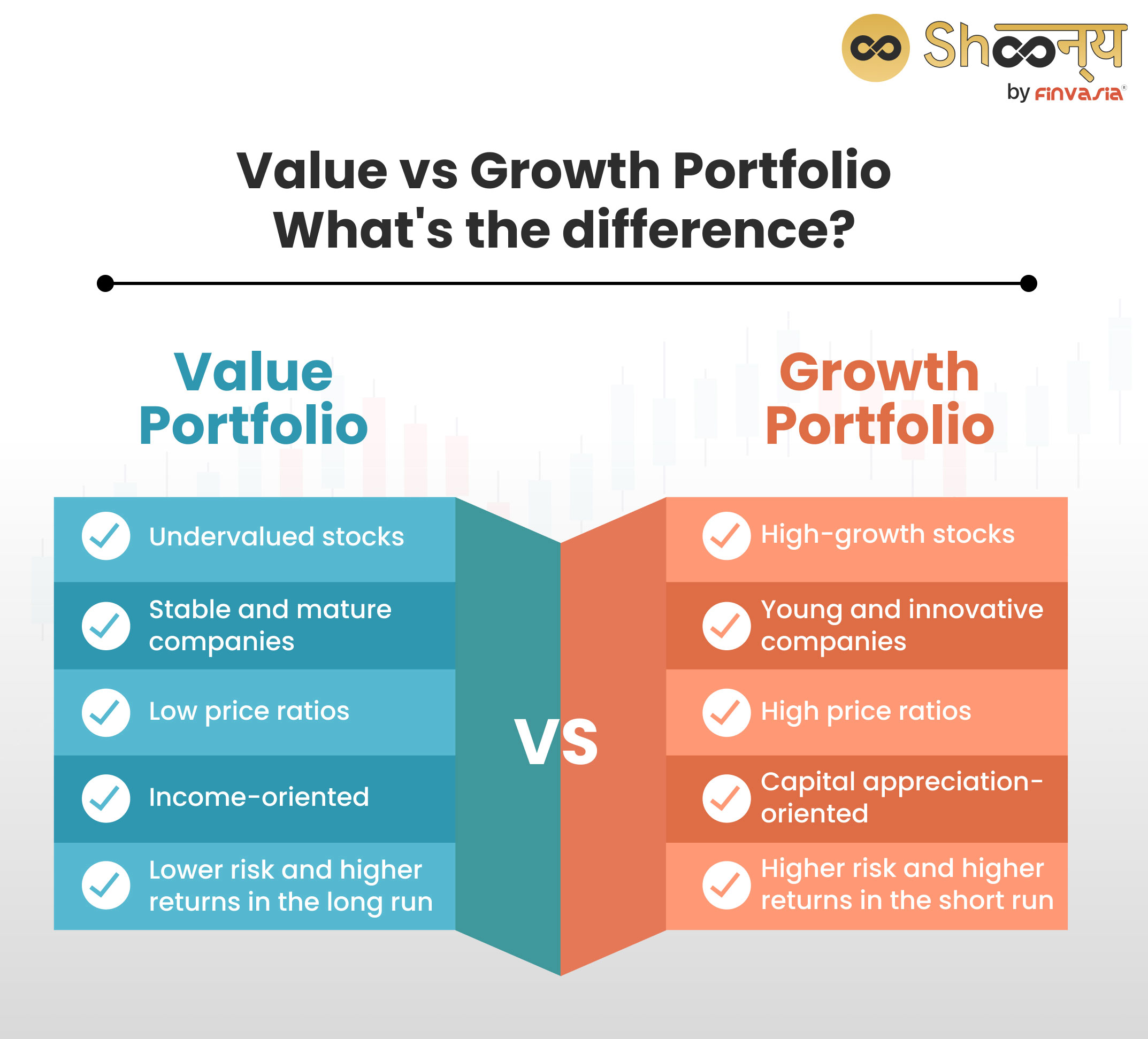
| Value Portfolio | Growth Portfolio |
| Contains stocks that are undervalued by the market | Contains stocks that have high growth potential |
| Focuses on stable and mature companies that pay dividends | Focuses on young and innovative companies that reinvest earnings |
| Trades at low prices relative to earnings, book value, or cash flow | Trades at high prices relative to earnings, book value, or cash flow |
| Offers lower risk and higher returns in the long run | Offers higher risk and higher returns in the short run |
| Performs better in bearish or sideways markets | Performs better in bullish or upward markets |
Portfolio Examples in the Stock Market
To illustrate the different types of portfolios in the stock market, let us look at some portfolio examples.
Conservative Portfolio
If you are looking to invest in the stock market and do not want to take a lot of risk, this one is for you.
A conservative portfolio in the stock market can include a mix of large-cap stocks, fixed-income securities, mid-cap stocks, and cash equivalents.
- Large-cap stocks provide stability, with investments in well-established companies boasting stable earnings and low volatility.
- Fixed-income securities, such as government bonds or high-rated corporate bonds, offer stability and regular income.
- Maintaining cash or cash equivalents within the portfolio ensures liquidity to capitalise on opportunities or handle emergencies.
Growth-Oriented Portfolio
If you’re aiming for significant growth potential in the stock market, consider a growth-oriented portfolio.
It can include large-cap, mid-cap, and small-cap stocks, along with sector-specific funds.
- Large-cap stocks offer stability.
- Mid-cap and small-cap stocks offer higher growth potential but increased risk.
- Sector-specific funds target high-growth sectors like technology or healthcare.
- Diversifying into international equities provides additional growth opportunities from foreign markets.
Dividend-Focused Portfolio
A dividend-focused portfolio suits investors seeking regular income.
It may include large-cap dividend-paying stocks, REITs, bonds, and utility stocks.
Investors seeking stable returns over time may opt for a growth-oriented portfolio. This type often includes stocks of companies with strong potential for capital appreciation.
- Large-cap dividend-paying stocks offer consistent income through dividends.
- REITs provide dividends and exposure to the real estate sector.
- Bonds, including government and corporate bonds, offer stability and fixed income.
- Utility stocks, known for stable dividends, can further enhance the income focus.
How to Create and Manage Your Portfolio in the Stock Market
Creating and managing your portfolio in the stock market is not a one-time activity but a continuous process.
It requires planning, research, monitoring, and review.
Here are some steps that can help you create and manage your portfolio in the stock market:
• Define your investment objectives: The first step is to define your investment objectives.
Find out the answers for yourself:
- Why are you investing?
- How much do you want to invest?
- How long do you want to invest?
- What returns do you expect from your investments?
Your investment objectives will help you understand the level of risk you are comfortable with.
Thus, decide the proportion of different assets in your portfolio.
• Choose your portfolio type: The next step is to choose your portfolio type.
You can choose one income, value, and growth.
• Select your portfolio assets: The third step is to select your portfolio assets.
You must do this based on your portfolio type.
You can choose from stocks, bonds, mutual funds, ETFs, bonds, currencies, and other securities.
This choice should depend on your risk-return expectations and tax implications of each.
Invest in all segments, including stocks, bonds, Mutual funds, currency, commodities and more, with a free demat account!
• Monitor and review your portfolio: The final step is to review your portfolio in the stock market.
Remember, this should be done regulalry.
You must check whether it is performing as per your expectations.
Or whether it is aligned with your investment objectives, risk profile, and asset allocation.
Conclusion
Portfolio in the stock market is a powerful tool that can help you achieve your financial goals. By understanding the meaning, types, and examples of portfolio in the stock market, you can create and manage your own portfolio.
Remember, a stock market portfolio offers benefits like diversification, flexibility, liquidity, and tax efficiency.
FAQs| Portfolio in the Stock Market
A stock portfolio is a collection of stocks that you own and manage. To make a stock portfolio, you need to decide how much money you want to invest, what kind of stocks you want to buy, and how you want to diversify your holdings.
A good stock portfolio is one that meets your investment objectives, matches your risk appetite, and performs well in different market conditions. It should have a mix of stocks from different sectors, industries, and regions.
A 33 33 33 investment strategy is a portfolio allocation strategy that divides your assets equally between stocks, bonds, and alternative investments, such as real estate, private equity, or venture capital.
______________________________________________________________________________________
Disclaimer: Investments in the securities market are subject to market risks; read all the related documents carefully before investing.








