Hard Currency Example| Learn Hard Currency vs Soft Currency

Currency is a huge part of our daily life. Be it food, groceries, trades, or stocks, everything matters because of currency. The currency market is vast and complex, with various terms and concepts that can be confusing. Among these, the terms ‘hard currency’ and ‘soft currency’ stand out as critical distinctions. They affect the investment decisions of individuals and businesses alike.
What are hard currency and soft currency, and how do we understand hard currency vs. soft currency?
Let us take a look!
What is Hard Currency?
Hard currency refers to stable and reliable currencies that are issued by developed countries. These are widely accepted around the world. People trust these currencies because they are not prone to sudden drops or rises in value.
Invest in currencies, commodities, mutual funds, and more with a free Demat account.
Investors and businesses prefer hard currencies like the US dollar, euro, or Japanese yen. This is because they are stable. This stability makes transactions and investments more predictable and secure.
Factors Affecting Hard Currency
Several factors determine whether a currency is considered ‘hard’:
- Political stability and good fiscal policies strengthen a currency.
- Maintaining purchasing power over time enhances currency stability.
- Central bank policies on inflation and currency stability are crucial.
- Social and military stability in a country supports a strong currency.
Advantages of Hard Currency
Hard currencies have several benefits:
- They maintain value over time, serving as a secure way to store wealth.
- They are easily traded on the forex market, providing flexibility for international transactions.
- Countries with hard currencies enjoy more purchasing power abroad and cheaper imports.
Disadvantages of Hard Currency
However, there are drawbacks to hard currencies:
- A strong currency can make a country’s exports more expensive and less competitive globally.
- It may lead to reduced domestic demand and a current account deficit if exports decline.
- Importers in countries with weaker currencies may face challenges due to the strength of hard currencies.
Before we understand hard currency vs soft currency, let us see what is soft currency!
Understanding Soft Currency
It is less stable and has limited acceptance outside its country of origin. These currencies are often subject to inflation and depreciation due to economic instability.
Soft currency fluctuates frequently and reacts sharply to a country’s political or economic situation. Experts often term it as a weak currency because of its unstable nature. They lead to high volatility in exchange rates, which makes them undesirable for foreign exchange dealers.
As a result, they are the least preferred for international trade or holding reserves.
Advantages of Soft Currency
Here are a few benefits of soft currency:
- It boosts export competitiveness as goods become cheaper for foreign buyers.
- It is a source of attractiveness for foreign investment due to lower asset prices.
Disadvantages of Soft Currency
Here are some downsides of soft currency
- The high amount of volatility increases investment risk.
- Economic instability can negatively impact investment and growth.
Hard Currency Vs Soft Currency| Example
Let us take a quick look at the difference between hard currency and soft currency with the help of an example:
Hard Currency Example
An example of a hard currency is the US dollar (USD). It enjoys global recognition and acceptance for international transactions and investments. It also acts as a reserve currency by many countries. Due to its relative stability compared to other currencies, businesses and investors worldwide prefer using the USD for global trade and financial transactions.
You must have heard about global commodities, such as oil and gold, being priced in US dollars.
Other examples include the Euro (EUR), British pound sterling (GBP), Japanese yen (JPY), and Swiss franc (CHF).
Soft Currency Example
Conversely, the Zimbabwe Dollar (ZWL) serves as a soft currency example because of its high volatility. Similarly, the Venezuelan Bolivar (VEF) is affected by high inflation rates, making it a soft currency.
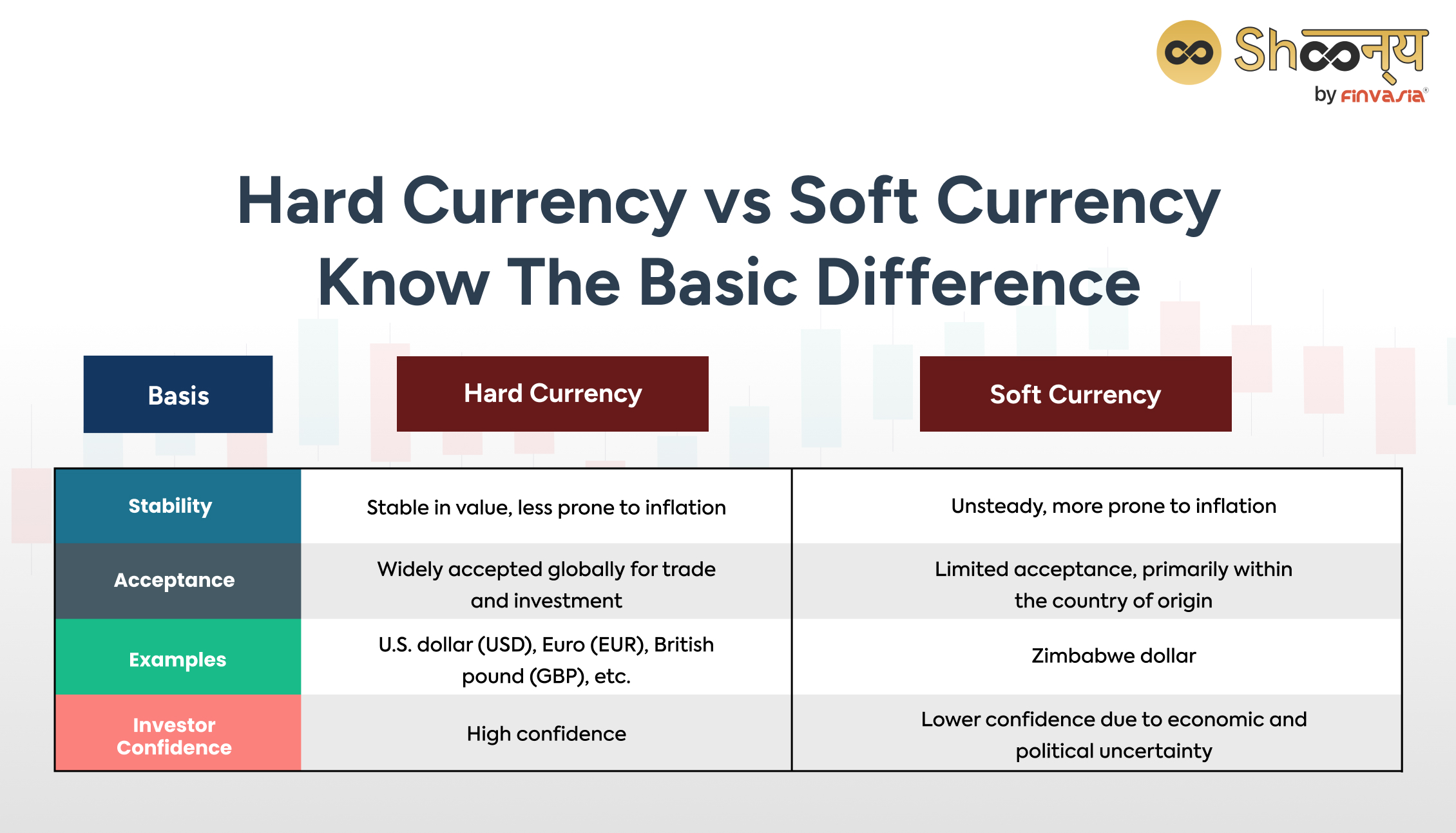
Let’s compare hard currency with soft currency.
Hard currency is stable and widely accepted, like a rock in the sea, while soft currency fluctuates more due to economic instability.
Soft currencies often come from countries with less stable economies, which makes people hesitant to use or hold them.
Stability and Confidence
Hard Currency: Known for stability, it instils confidence among investors, both domestic and international.
Soft Currency: Prone to fluctuations and volatility, leading to uncertainty among investors.
Global Acceptance
Hard Currency: It is accepted worldwide for trade. Thus making it a preferred choice for international transactions.
Soft Currency: Limited acceptance beyond its borders, hindering international trade.
Inflation Risk
Hard Currency: Less susceptible to inflation, preserving its value over time.
Soft Currency: Vulnerable to inflation, potentially eroding its value.
Hard Currencies vs Soft Currencies| Key Things to Note
Indian investors need to consider the choice between hard and soft currencies carefully when making investment decisions.
- Diversifying investments in hard currencies can provide stability and protection against INR depreciation.
- When considering foreign investments, understanding currency risks is crucial to mitigate potential losses.
- Investors can explore hedging strategies to protect their portfolios from currency fluctuations.
Conclusion
In finance, hard currencies are the strong foundation of global trade, known for their stability and widespread trust. In contrast, soft currencies are much less stable. This difference is vital for investors because it affects how they manage risks and make decisions.
FAQs| Hard Currency vs Soft Currency
Hard currency is money from a politically and economically stable country that is widely accepted globally, while soft currency is less stable.
India does not have a hard currency. The Indian Rupee is not considered a hard currency due to its fluctuating value and limited international acceptance.
Gold is not a currency but is often considered a hard asset that holds intrinsic value.
It’s possible but rare. Soft currencies require significant economic reforms to become hard currencies.
Currency exchange rates can impact the cost of imports and exports, affecting trade balance and economic stability.
______________________________________________________________________________________
Disclaimer: Investments in the securities market are subject to market risks; read all the related documents carefully before investing.








