All About Debentures: Types, Redemption, Advantages & More

Have you been looking for a fixed-income investment? The one that offers regular interest payments and a high degree of safety? Ever heard about debentures? They are long-term debt instruments issued by corporations or governments to raise funds for their projects or operations. But what are the types of debentures in which you can invest?
Let us take a look!
What are Debentures?
These are long-term debt instruments issued by corporations or governments to raise capital. They usually have a fixed interest rate and a maturity date.
Debentures are like loans that companies take from people like you. When you buy a debenture, you’re lending money to the company. In return, the company promises to pay you back the money with interest at a fixed time in the future.
It’s a way for companies to raise funds for their projects or expansions without giving away ownership. So, when you invest in debentures, you’re basically becoming a lender to the company instead of a shareholder.
Debentures examples in the Indian market include those issued by companies like Tata Motors, Reliance Industries, and Infosys.
These companies raise funds by offering debentures to investors. When you invest in these debentures, you’re essentially lending money to these companies in exchange for regular interest payments. So, it’s like you’re helping them grow while earning interest on your investment.
But what is the difference between bonds and debentures?
Let us understand!
Exploring the Difference Between Bonds and Debentures
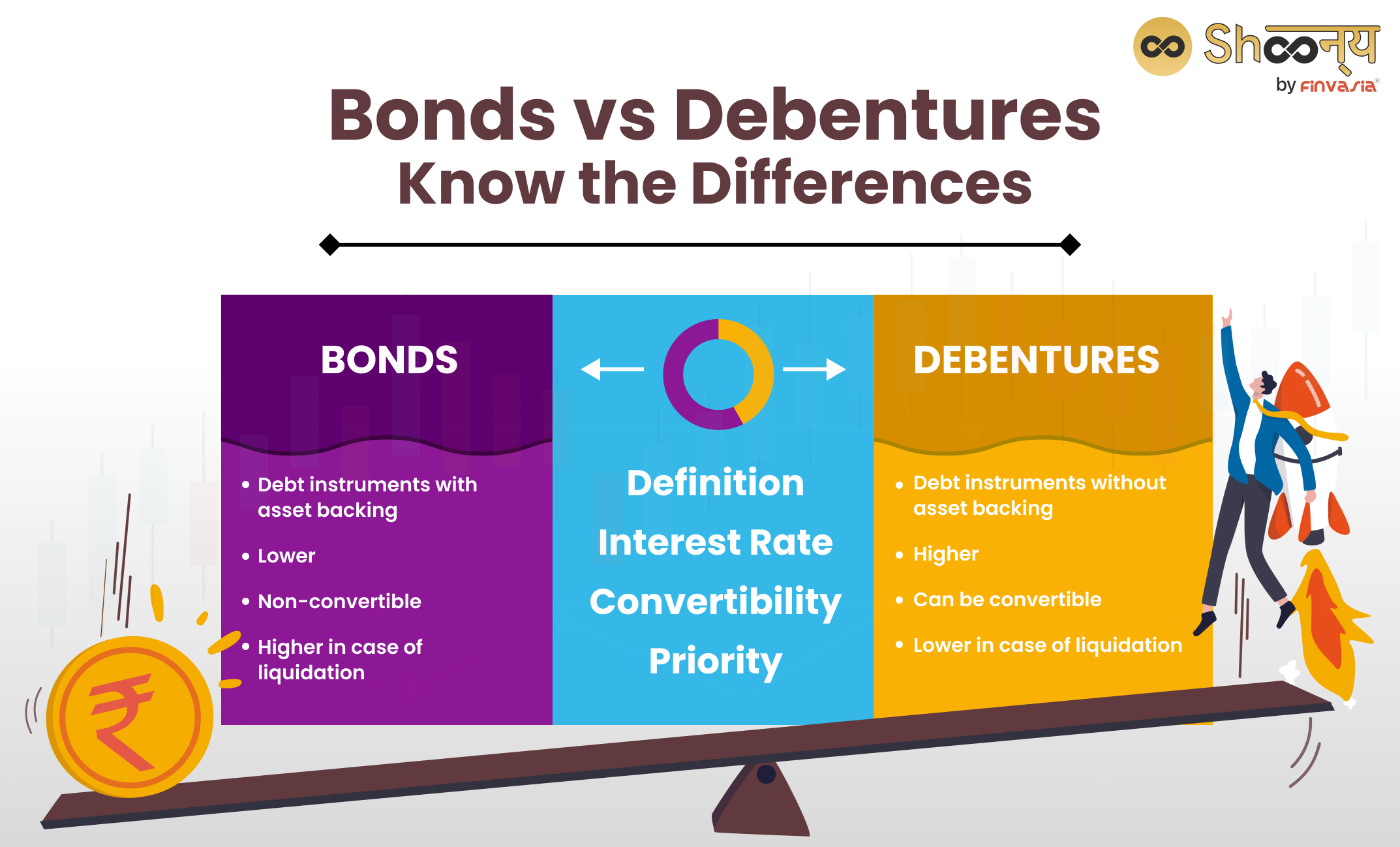
| Basis | Bonds | Debentures |
| Definition | Debt instruments with asset backing | Debt instruments without asset backing |
| Security | Secured by assets | Unsecured (depends on creditworthiness) |
| Interest Rate | Lower | Higher |
| Convertibility | Non-convertible | Can be convertible |
| Priority | Higher in case of liquidation | Lower in case of liquidation |
You may wonder what to choose when we talk about fixed-income securities. Let’s take a look at the key differences between bonds and debentures.
Security
- Bonds are secured by the assets of the issuer, providing a higher level of security to the investors.
- Debentures are unsecured and depend on the creditworthiness of the issuer, making them riskier than bonds.
Interest Rate
- Bonds usually have a lower interest rate as they are less risky and more stable.
- Debentures usually have a higher interest rate than bonds, as they are more risky and less stable than bonds.
Convertibility
- Bonds are usually non-convertible, meaning they cannot be converted into equity shares or other securities of the issuer.
- Debentures can be convertible or non-convertible, meaning they can or cannot be converted into equity shares or other securities of the issuer.
Priority
- Bonds have a higher priority than debentures in the event of liquidation of the issuer, as they are secured by the assets of the issuer.
- Debentures have a lower priority than bonds in the event of liquidation of the issuer, as they are unsecured and rank after the secured creditors.
Exploring the Types of Debentures
There are different types of debentures based on their security, tenure, convertibility, coupon rate, registration, and priority.
Convertible Debentures
These grant the holder the right to convert them into equity shares of the issuing company. You can do it at a predetermined conversion ratio and within a specified time frame.
So, if the company does well, you can switch your these for shares and become a part-owner.
Non-Convertible Debentures (NCDs)
These are not convertible into equity shares. These remain as debt instruments until maturity. The issuing company repays the principal amount along with the agreed-upon interest.
They stick to being loans until they mature, and the company pays you back with interest.
Secured Debentures
These are backed by collateral, such as the assets of the issuing company.
In case of default, the debenture holders have a claim on the specified assets.
So, if the company can’t pay you back, you can claim those assets to get your money back.
Unsecured Debentures
Also known as ‘Debentures without a charge,’ these are not backed by any collateral. They rely solely on the creditworthiness and reputation of the issuing company.
These are riskier. They aren’t backed by any specific assets, so if the company can’t pay, you might struggle to get your money back.
Redeemable Debentures
These debentures are like loans with a fixed repayment date. The issuer agrees to pay back the principal amount along with interest on a specified date.
This is just like how you repay a loan by a certain deadline.
Non-Redeemable Debentures
These debentures don’t have a fixed repayment date. It’s like lending money to someone with no set deadline for them to pay you back.
They might pay you interest regularly. But there’s no promise of getting your principal amount back by a specific date.
Redemption of Debentures
Redemption of debentures is like returning borrowed money.
When a company issues these, it’s like borrowing cash from investors.
But at some point, the company pays back that money. This payment-back process is called redemption. It’s similar to repaying a loan.
So, when a company redeems its debentures, it’s basically returning the money it borrowed from investors.
It is the process through which a company repays the amount borrowed by redeeming or buying back the debentures issued to investors. It involves returning the principal amount along with any accrued interest or premium to the debenture holders. This extinguishes the company’s obligation towards the debenture holders.
There are various methods of redemption:
- Payment in a lump sum
- Payment in instalments,
- Purchase in the open market and conversion into shares.
Advantages of Debentures
Here are some of the reasons you should consider debentures:
- Flexibility in Terms
Companies issuing debentures have flexibility in setting terms such as interest rates and redemption periods. This allows them to tailor the terms to suit their financial needs.
- No Dilution of Ownership
Unlike equity financing, debenture holders do not have voting rights or ownership claims. This ensures that existing shareholders’ control and ownership percentages remain unchanged.
- Tax Deductibility
Interest payments on debentures are tax-deductible expenses for the issuing company. It reduces its overall tax liability and enhances its financial efficiency.
Disadvantages of Debentures
Here are certain cons of buying debentures
- High-Interest Payments
These often require regular interest payments. This can impose a considerable financial burden on the issuing company.
- Risk of Default
Since these are unsecured, investors bear the risk of default if the issuing company fails to meet its financial obligations.
- Impact on Credit Rating
Issuing debentures can increase the company’s debt levels. This affects its credit rating and ability to secure future financing at favourable terms.
Conclusion
Debentures are different from bonds in terms of security, interest rate, convertibility, and priority. They are suitable for investors who are looking for a stable and predictable income stream with low risk and high priority. However, investors should also be aware of the risk of default, the impact on credit rating, and the tax implications of investing in debentures.
FAQs| What are Debentures
A bond is a debt instrument that is secured by the issuer’s assets, while a debenture is an unsecured debt instrument that relies on the issuer’s creditworthiness.
People use debentures as a way of raising long-term funds for their projects or operations without diluting their ownership or control. Debentures also offer a lower cost of capital than equity, as the interest payments are tax-deductible.
Debentures offer several benefits to both the issuers and the investors. For the issuers, debentures provide flexibility in terms of interest rate, maturity period, and convertibility. For the investors, debentures provide a regular and stable source of income.
______________________________________________________________________________________
Disclaimer: Investments in the securities market are subject to market risks; read all the related documents carefully before investing.








