If you are a beginner in the stock market, you must be curious to know the ways to invest in companies. Shares and debentures are two routes. But do you know what they mean and how they differ from each other? These are two common methods for companies to raise funds from the public, but there is a huge difference between shares and debentures.
In this blog, we will explain the key difference between shares and debentures and help you understand their respective features, types, and more.
Shares Meaning
Shares represent the units of your ownership in a company. When a company issues shares, it is offering a part of its share capital to the investors, who then become shareholders or owners of the company.
Understanding Shares Meaning with an Example
imagine you start a pizza joint with a friend. You both put in money. Now, to keep it fair, you decide to split the ownership into shares.
Each share is like a slice of the pizza (or the business, in this case). The more shares you have, the bigger piece of the business you own.
In the stock market, companies like Infosys or Tata Motors are like these pizza joints. They’re divided into millions of slices (shares).
When you buy shares of a company, you’re basically buying a piece of that business. If the business does well, your share’s value might go up. If it doesn’t, well, you might have a less valuable slice.
Debentures Meaning
It represents a type of debt instrument issued by corporations or governments to raise capital. When a company issues debentures, it means that it is borrowing money from investors. However, they do it with a promise to repay the principal amount along with interest at a specified future date.
- It is a document that acts as proof of debt.
- It contains the terms and conditions of the loan, such as the amount, the interest rate, the maturity date, the security, if any, etc.
- Debentures are a form of long-term financing for a company that needs funds for expansion, diversification, or modernisation.
Debentures have lower interest rates than other forms of borrowing, and they are tax-deductible expenses.
Understanding Debentures Meaning with an Example
Imagine you want to expand your pizza place, but you need more cash. You can’t call up your partner. So, you decide to borrow money from someone else.
This is where debentures come in. You will borrow money from someone willing to invest in your pizza business with a promise to pay him back at a future date with interest.
Companies like Reliance, HDFC, Tata, or even government organisations may issue debentures to raise funds.
When you buy a debenture, you’re basically lending money to the company.
In return, the company promises to pay you back with some interest after a certain period.
When we distinguish between ‘shares’ and ‘debentures,’ shares grant ownership in a company, while debentures entail temporary lending.
Remember, the stock market is like a giant pizza party, and companies like Infosys, Tata Motors, Reliance, and HDFC are just some of the places where you can get a slice or lend them some dough!
Difference between Shares and Debentures in the Indian Stock Market
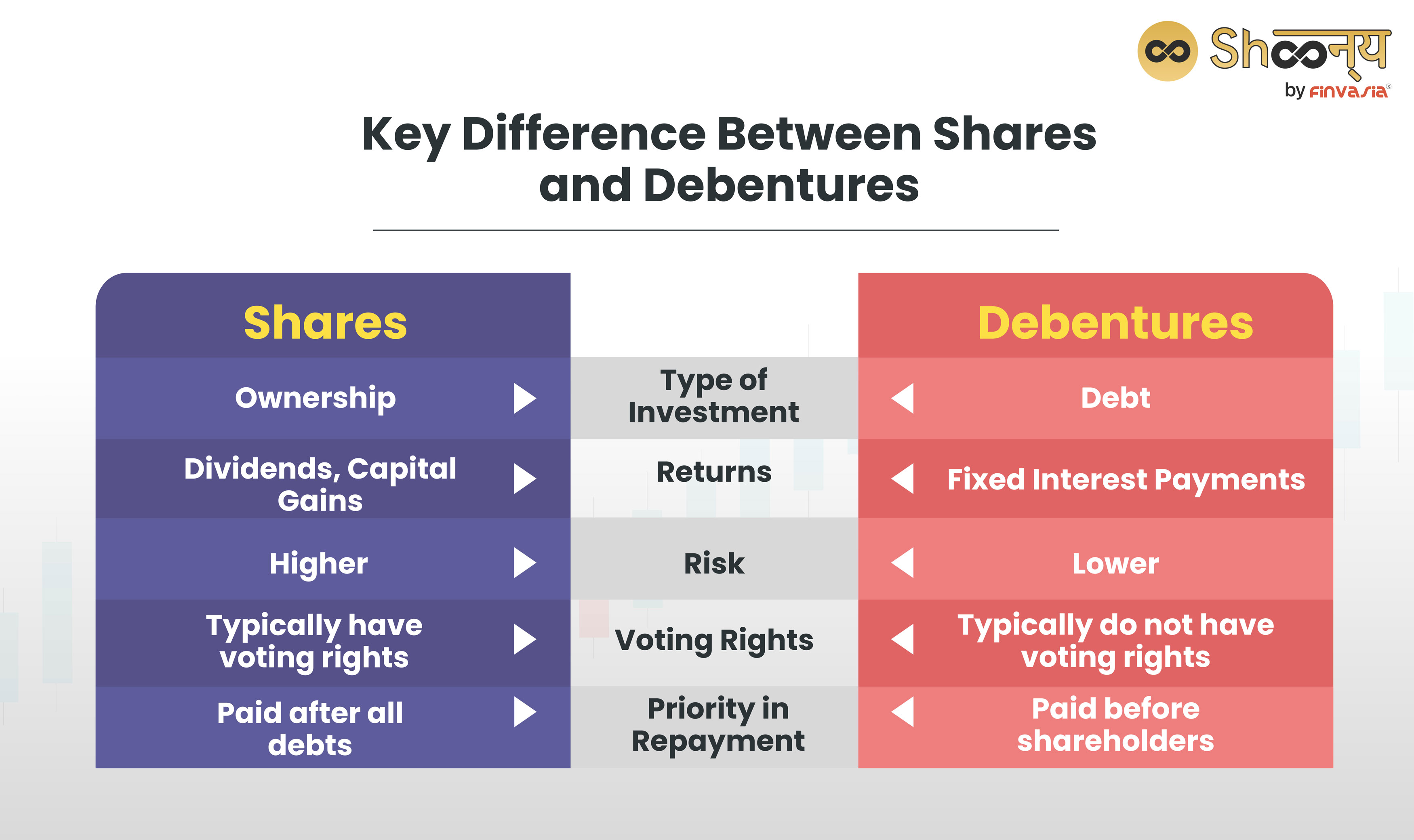
Here is a brief table to distinguish between shares and debentures.
| Basis | Shares | Debentures |
| Nature of Capital | Company-owned capital | Borrowed capital of the company |
| Holder | Shareholder | Debenture holder |
| Ownership Status | Shareholders are owners of the company | Debenture holders are creditors |
| Representation of Capital | Represents a part of the company’s capital | Represents a loan to the company |
| Voting Rights | Shareholders have voting rights | Debenture holders do not have voting rights |
| Dividends | The company pays dividends to shareholders | The company pays interest to debenture holders |
| Dividend Source | Dividends paid only out of profits | Interest can be paid even if there is no profit |
| Tax Deductibility | Dividends are not allowed as a deduction from profit | Interest is allowed as a deduction from profit |
| Convertibility | Not convertible into debentures | Can be convertible into shares |
| Repayment in Winding Up | Repaid after paying off liabilities in winding up | Repaid before shares in winding up |
| Charge on Assets | Does not carry any charge on the assets | May carry a charge on the assets |
| Trust Deed Requirement | No trust deed is executed | A trust deed must be executed |
What is the Key Difference between Shares and Debentures?
Shares represent the capital of the company, while debentures represent the debt of the company. But, there are so many who still cannot distinguish between shares and debentures.
Let’s clarify!
- Voting Rights: Shareholders can vote on company matters; debenture holders cannot.
- Returns: Shareholders may receive dividends based on profits; debenture holders get fixed interest payments.
- Risk: Shares carry higher risk and rewards; debentures are generally safer with fixed returns.
- Repayment: In company closure, debenture holders are paid first; shareholders are paid last from remaining assets.
- Conversion: Some debentures can convert to shares; shares cannot become debentures.
- Tax: Interest on debentures can be tax-deductible; dividends on shares are not.
What’s the biggest difference between shares and debentures?
Shares have high liquidity as you can buy and sell them easily. However, debentures have low liquidity as they are usually long-term and not easily transferable.
Debentures vs Shares: Know the Types
If you believe you can now easily distinguish between shares and debentures, here’s something more to learn!
They differ in their types:
Types of Debentures
• Secured debentures: These debentures have some assets of the company as a guarantee.
If the company fails to pay back the money, the investors can sell the assets and get their money back.
• Unsecured debentures: These have no assets of the company as a guarantee.
If the company fails to pay back the money, the investors have no right to sell any assets and may lose their money.
These debentures are riskier and have higher interest rates than secured debentures.
• Convertible debentures: You can convert these debentures into shares or other securities of the company at a fixed rate.
These debentures have lower interest rates than non-convertible debentures.
• Non-convertible debentures: These are debentures that cannot be changed into shares or other securities of the company.
These debentures have higher interest rates than convertible debentures.
• Registered debentures: These debentures have the name and details of the investor who owns them.
You can transfer them to someone else only by signing a document. The company pays the interest and the principal only to the investor who owns them or their nominee.
• Bearer debentures: You can transfer these debentures to someone else by just delivering them. The company pays the interest and the principal to whoever presents the document.
Types of Shares
There are two types of shares that are commonly traded:
Equity Shares:
- Owners (shareholders) have voting rights in company decisions.
- Dividends are not fixed and depend on the company’s profits.
- Equity shares are transferable.
Preference Shares:
- Owners have preferential rights (distribution of dividend on priority basis) to receive dividends and claim assets in case of liquidation.
- Usually non-transferable and non-voting unless there’s a default on dividend payments.
- Preference shareholders receive a fixed rate of dividend before equity shareholders.
- They are further classified into types such as, cumulative, non-cumulative, participating, non-participating, convertible, and non-convertible.
Shareholders and Debenture Holders
Shareholders and debenture holders are two types of investors who provide funds to a company.
However, they have different roles and responsibilities in relation to the company.
Shareholders
Shareholders are the owners of the company who have invested their money in buying the shares of the company.
They have a stake in the company’s share capital. They have the right to a proportionate share of the profits and assets of the company.
Debenture Holders
Debenture holders are the creditors of the company who have lent their money to the company by buying the debentures of the company.
They have a claim on the company’s debt. They have the right to a fixed rate of interest and the repayment of the principal amount.
What is the Difference Between Shareholders and Debenture Holders
Here is the basic difference between shareholders and debenture holders:
• Shareholders are the owners of the company. However, debenture holders are the lenders of the company.
• Shareholders have voting rights and can influence the management and decisions of the company. Debenture holders, on the other hand, do not have any such rights or powers.
• Shareholders receive dividends as a share of the profits of the company. Debenture holders receive interest as a fixed return on their investment.
• Shareholders have a residual claim on the assets and income of the company after paying off all the liabilities. On the flipside, debenture holders have a prior claim on the assets and income of the company before paying off any other creditors.
Debentures vs Stocks: Which is Better?
Now, with the highlighted difference between debentures and shares, you must be considering which to invest in.
Debentures are like loans – you give the company money, and they promise to pay you back with interest, no matter how well the company does.
It’s a bit safer, but you can’t easily sell it or get your money back quickly.
Shares, on the other hand, are riskier. When you buy shares, you’re buying a piece of the company. If the company does well, you can make money through dividends and selling the shares for a profit. But if the company struggles, you might lose money.
Deciding between debentures and shares depends on how much risk you’re comfortable with. Debentures are safer but give lower returns, while shares can be riskier but have the potential for higher rewards.
No clear winner here – it’s all about what fits you best.
FAQs| Difference Between Shares and Debentures
A shareholder owns a piece of the company and may have voting rights, while a debenture holder lends money to the company and receives fixed interest payments without ownership or voting rights.
Preference shares represent ownership with preferential rights to dividends and assets, whereas debentures are debt instruments that pay fixed interest but don’t confer ownership or voting rights.
An IPO (Initial Public Offering) is when a private company goes public by offering shares to the public. In contrast, debentures are debt securities issued by a company, representing loans from investors.
A share is the smallest unit of ownership in a company, while a stock is a collection of shares. In essence, owning shares means owning parts of individual companies, and owning stocks means having a portfolio of various company shares.
Yes, some debentures can be converted into shares. These are called convertible debentures. After a certain period, they can be turned into company shares at a set price.
______________________________________________________________________________________
Disclaimer: Investments in the securities market are subject to market risks; read all the related documents carefully before investing.

