Portfolio management is like being the conductor of your financial orchestra. Just as a conductor brings together different instruments to create a harmonious symphony, a portfolio manager assembles a diverse mix of investments to achieve a specific financial goal. The portfolio manager is responsible for choosing the right mix of investments, allocating assets, and rebalancing the portfolio to optimise performance and manage risk. So if you want to make beautiful music with your money, consider hiring a portfolio manager to help you hit all the right notes.
Definition of PMS- (Portfolio Management Services)
Portfolio management services (PMS) are professional investment management services offered by financial institutions or independent investment firms. These firms manage investment portfolios on behalf of individual or institutional investors. The benefits of PMS investment vary as the portfolio managers offer various services, including portfolio construction, asset allocation, and ongoing portfolio management. PMS providers use their expertise and resources to create customised portfolios tailored to each investor’s specific financial goals and risk tolerance. PMS can be a valuable tool for investors who want to maximise their returns and minimise risk but don’t have the time, knowledge, or access to manage their own investments.
The first step to experiencing portfolio management services is the selection of your portfolio manager. This seems easy, but let us tell you, it is the hardest task while stepping into the stock market.
Selecting a portfolio manager can be challenging for those new to the stock market. Therefore, you should research before choosing a portfolio manager and avoid making the common mistakes that ultimately result in your loss.
Are buying Stocks and Creating Portfolios different?
Yes, buying stocks and creating a portfolio are different concepts. Buying stocks refers to the act of purchasing shares of a particular company or company. On the other hand, a portfolio is a collection of investments, including stocks, bonds, and other financial instruments. An investor may choose to buy stocks as part of their portfolio to diversify their holdings and manage risk. Creating a portfolio involves deciding which investments to include, how much to allocate to each investment, and how to rebalance the portfolio over time to meet the investor’s financial goals.
Pros and Cons of PMS
There are both advantages and disadvantages to using portfolio management services (PMS). Some of the potential advantages include
- Expertise: PMS providers have professional expertise and resources that can help investors make informed investment decisions. Investors who lack the time or knowledge to manage their own investments may find this service particularly useful.
- Customization: PMS providers can create customised portfolios tailored to each investor’s specific financial goals and risk tolerance. This can help investors achieve their financial objectives more effectively.
- Diversification: PMS providers can help investors diversify their portfolios and manage risk by allocating assets across different sectors, industries, and geographies.
- Convenience: PMS providers handle the day-to-day management of the portfolio, which can save investors time and effort.
However, there are also some potential disadvantages of PMS to consider:
- Cost: PMS can be more expensive than managing investments on your own, as you’ll be paying for the expertise and services of the PMS provider.
- Lack of control: By outsourcing the management of your portfolio to a PMS provider, you’ll be giving up some control over your investments.
- Performance risk: While PMS providers strive to achieve the best possible returns for their clients, there is always a risk that the portfolio will underperform.
- Misalignment of interests: There is a potential for a conflict of interest if the PMS provider’s interests are not aligned with those of the investor.
Overall, whether or not PMS is a good choice for you will depend on your individual financial situation and goals. It’s important to carefully consider the potential advantages and disadvantages before deciding whether to use a PMS provider.
Does PMS sound more like Mutual Fund? We bet! Of course, it does.
Portfolio management services (PMS) and mutual funds are both investment management products that provide professional management of a portfolio of securities.
However, there are some key differences between the two:
Mutual Funds vs PMS- What’s the Difference?
- Customization: PMS is typically more customised than mutual funds, as PMS providers will create a portfolio specifically tailored to the financial goals and risk tolerance of each individual investor. On the other hand, mutual funds investments are typically more standardised, with a fixed investment mandate that applies to all investors.
- Fees: PMS providers typically charge higher fees than mutual funds, as they offer more personalised and specialised services. Mutual funds generally have lower fees, as they are more standardised and serve a larger number of investors.
- Minimum investment: PMS typically requires a higher minimum investment than mutual funds. This is because PMS is typically geared towards high net worth or institutional investors with more money.
- Access: PMS may provide access to a wider range of investment opportunities, including private equity and hedge funds, which are not typically available through mutual funds.
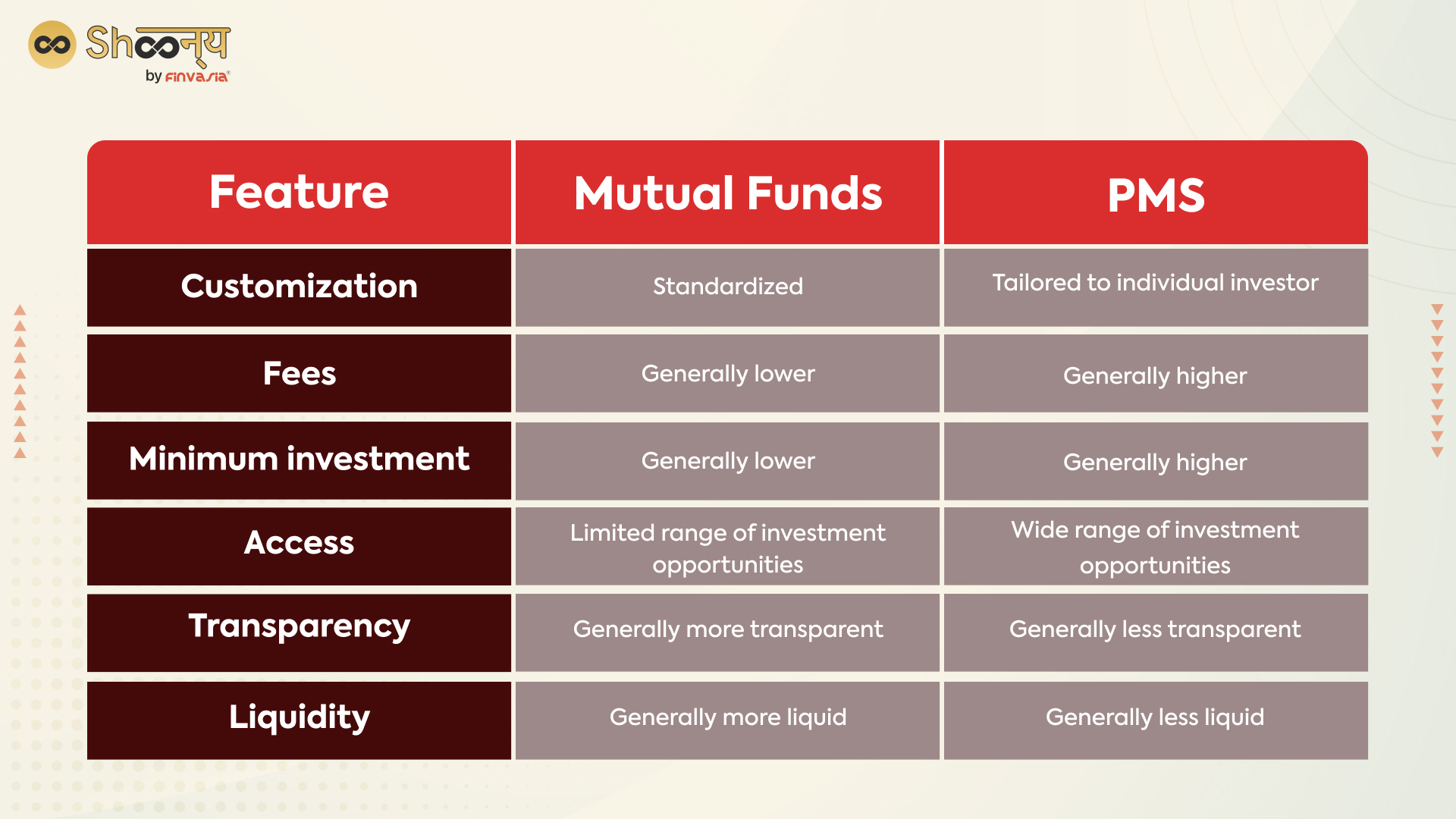
Overall, PMS and mutual funds are both options for investors who want professional management of their investments, but they differ in terms of customisation, fees, minimum investment, and access to investment opportunities.
I am afraid to invest in PMS. How can I trust a person while handling my money? Is PMS risky?
Like any investment, portfolio management services (PMS) carry some level of risk. There is always a chance that the portfolio will underperform or that the value of the investments will decline. You may be exposed to one of the portfolio risks. However, it is always suggested that you calculate portfolio risk before making your final decision.
For instance, the PMS manager may not align their interests with those of the investor, which could lead to conflicts of interest. It’s important to carefully evaluate the reputation and track record of the PMS provider and ensure that they understand your financial goals and risk tolerance before choosing to invest with them.
Here: take a look at our Financial Planning Guide to ensure that you carefully consider your financial situation and risk tolerance before deciding whether to invest in PMS.
Portfolio Diversification
It is generally advisable to diversify an investment portfolio by including a mix of various asset classes, such as equities, fixed-income securities, and cash equivalents. In addition to diversifying across asset classes, it’s also important to consider diversifying within each asset class. For example, if you hold a large number of equity mutual funds. In that case, you may want to consider diversifying among different sectors and market capitalisations to spread risk further, as all of the funds may be subject to market fluctuations.
The Best Option for Diversifying Portfolios
There are different strategies for diversifying a portfolio, and the best option will depend on your financial situation, risk tolerance, and investment goals. However, some common strategies for diversifying a portfolio include the following:
- Diversifying across asset classes: This can be achieved by including a mix of stocks, bonds, cash, and other asset classes in your portfolio.
- Diversifying within asset classes: Within each asset class, it’s important to consider diversifying among different sectors, market capitalisations, and geographic regions.
- Diversifying among investment vehicles: You may also want to consider using different types of investment vehicles, such as mutual funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), and individual securities, to diversify your portfolio further.
- Rebalancing your portfolio: It’s important to periodically review and rebalance your portfolio to ensure it continues to align with your investment goals. This may involve selling some assets and buying others to maintain your desired asset allocation.
PMS and Rebalancing of Portfolio
Rebalancing is a key component of portfolio management services (PMS). It involves adjusting the allocation of assets within a portfolio to maintain the desired level of risk and return.
There are several reasons why rebalancing may be necessary:
- To maintain the desired asset allocation: Over time, the performance of different asset classes can vary, which can cause the allocation of assets within a portfolio to drift from the target allocation.
- To manage risk: Rebalancing can help manage risk by ensuring that the portfolio is not overly concentrated in any one asset class or sector.
- To capture opportunities: Rebalancing can also help investors capture opportunities as they arise by selling underperforming assets and buying assets that are expected to perform well.
PMS providers typically handle the rebalancing of a portfolio on behalf of the investor. They will monitor the portfolio on an ongoing basis and adjust as needed to optimise performance and manage risk.
Some additional notes about Rebalancing:
Portfolio Management Strategies
There are many portfolio management strategies, and simultaneously types of PMS may be many; however, investors can use their best to diversify their portfolios, protect against market fluctuations, and achieve their financial goals. Here are three strategies that can be effective in these areas:
- Diversification: One of the most effective strategies for diversifying a portfolio is to allocate assets across different asset classes, sectors, and geographies. This can help reduce the impact of any single investment on the overall portfolio and can also help manage risk.
- Asset allocation: This involves determining a portfolio’s proportion of stocks, bonds, and money market instruments among different asset classes.
- Tactical asset allocation: Tactical asset allocation is a flexible investment strategy that actively adjusts the asset allocation within a portfolio based on market conditions and other factors. This can help investors protect their portfolios during market fluctuations and capture opportunities as they arise.
One of the most effective strategies is diversifying a portfolio.
Diversification can help reduce the impact of any single investment on the overall portfolio and can also help manage risk. For example, suppose you have a portfolio that is heavily weighted towards a particular sector or geography. In that case, you may be more vulnerable to economic or political events that affect that sector or region. By diversifying your portfolio, you can spread your risk across a wider range of investments, which can help protect against losses if any one investment performs poorly.
Heard the terms like Optimal Portfolio or Equal Weighted Portfolio?
Understanding the Optimal Portfolio Definition for Maximizing Investment Returns and Minimizing Risk
An optimal portfolio is a portfolio that is designed to maximise return for a given level of risk or to minimise risk for a given level of return. It is typically constructed using modern portfolio theory, a mathematical model that helps investors identify the combination of assets that will provide the highest expected return for a given level of risk.
Remember that an optimal portfolio is not a guarantee of success and that all investments carry some risk. It’s important to regularly review and adjust your portfolio as needed to ensure it continues to meet your investment goals.
What is an Equally Weighted Portfolio?
An equal-weight portfolio is a type of investment portfolio in which each security is given the same weight, regardless of its market capitalisation or other factors. An equal-weight portfolio is regularly rebalanced to maintain equal weightings of each security.
It’s generally a good idea to seek the advice of a financial advisor or portfolio manager when building an equally-weighted portfolio, as they can guide you about the securities to include and help you develop a customised investment plan.
Final Roadmap to Portfolio Management
Now, comes the most important question: Can I manage my finances on my own or, do I need a financial manager?
It is possible to manage your finances independently, but whether or not you need a financial manager will depend on your circumstances.
Here, you can check this article to decide better: Financial planning by yourself or through your financial advisor
Ultimately, the decision to hire a financial manager is a personal one and will depend on your individual needs and circumstances. If you decide to hire a financial manager, it’s essential to carefully research and choose a reputable and experienced professional who aligns with your investment goals and risk tolerance.
FAQs
The three types of portfolio management include Passive, which follows a predefined strategy, Active, involving frequent adjustments to beat the market, and Hybrid, combining both strategies.
Portfolio management involves selecting, monitoring, and rebalancing assets to meet investment objectives. For instance, a fund manager invests in stocks, bonds, and cash to create a diversified portfolio for investors.
Portfolio management is the art of making optimal investment decisions. Its benefits include achieving risk-return alignment, optimizing performance, reducing overall risk, and simplifying the investment process.
Portfolio management Sebi involves regulating and supervising portfolio management services (PMS) by India’s Securities and Exchange Board (SEBI). SEBI ensures transparency, accountability, and compliance among PMS providers.
The four types of portfolio management are Aggressive (high risks, high returns), Defensive (low risks, stable returns), Income (generating regular income), and Growth (investing in potential value appreciation).
Portfolio management includes Discretionary PMS (manager has full authority) and Non-discretionary PMS (manager consults the client before decisions).
Portfolio managers can be Fund managers (manage pooled money), Individual managers (customized portfolios), Team managers (group of experts), and Robo-advisors (algorithm-driven).
______________________________________________________________________________________
Disclaimer: Investments in the securities market are subject to market risks; read all the related documents carefully before investing.

