When it comes to Tax, the well-established rule is that no income can escape it, except in cases where your income is lower than the taxable threshold. In such circumstances, your income is exempt from Tax. However, you still need to follow the rule book and get your documentation right to ensure that you do not end up paying Tax to the income tax (I-T) department when you do not owe any.
TDS is Applicable to Various Incomes
Individual taxpayers have to mandatorily declare their earnings to the department on their own. You will feel the tax impact even at the time of receiving payments. Entities or persons making certain payments are obliged to deduct Tax at source (TDS) before handing out the money.
Examples are employers who pay salaries or banks that credit savings or fixed deposit interest to your account. In the case of salaried individuals, employers are responsible for calculating the TDS based on the applicable I-T slab. However, for income other than salary, TDS is typically applied at a fixed rate under the I-T Act 1961. This rate varies according to the nature and the source of income, as well as whether a Permanent Account Number (PAN) was provided or not.
Understanding TDS Thresholds
It’s important to note that the rate does not consider whether the income earned is taxable or not in the hands of the recipient. In some cases, TDS comes into play only if the income crosses a certain threshold.
For instance, TDS is to be deducted when the interest income earned exceeds Rs 40,000 and Rs 50,000 in a financial year for all resident assesses and resident senior citizens, respectively. Similarly, the threshold for TDS is Rs 5,000 in case of interest from corporate bonds.
However, in situations where TDS may be levied unnecessarily, or, in other words, where income is below the taxable limit, a taxpayer can utilise Form 15 G or 15 H to rectify this.
Rent TDS Limits in India
In India, Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) on rent payments is an essential component of the tax system. Individuals or Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs) who pay rent to landlords, especially for commercial or residential properties, need to be aware of the applicable TDS rules.
The TDS on rent comes into play when the monthly rent exceeds Rs 50,000 or part of a month. It is crucial to understand that this rule applies to individuals and HUFs who are not liable for a tax audit. If the rent surpasses this threshold, the tenant is responsible for deducting TDS at a rate of 5% of the rent paid or credited to the landlord.
Role of Form 15 G Mean
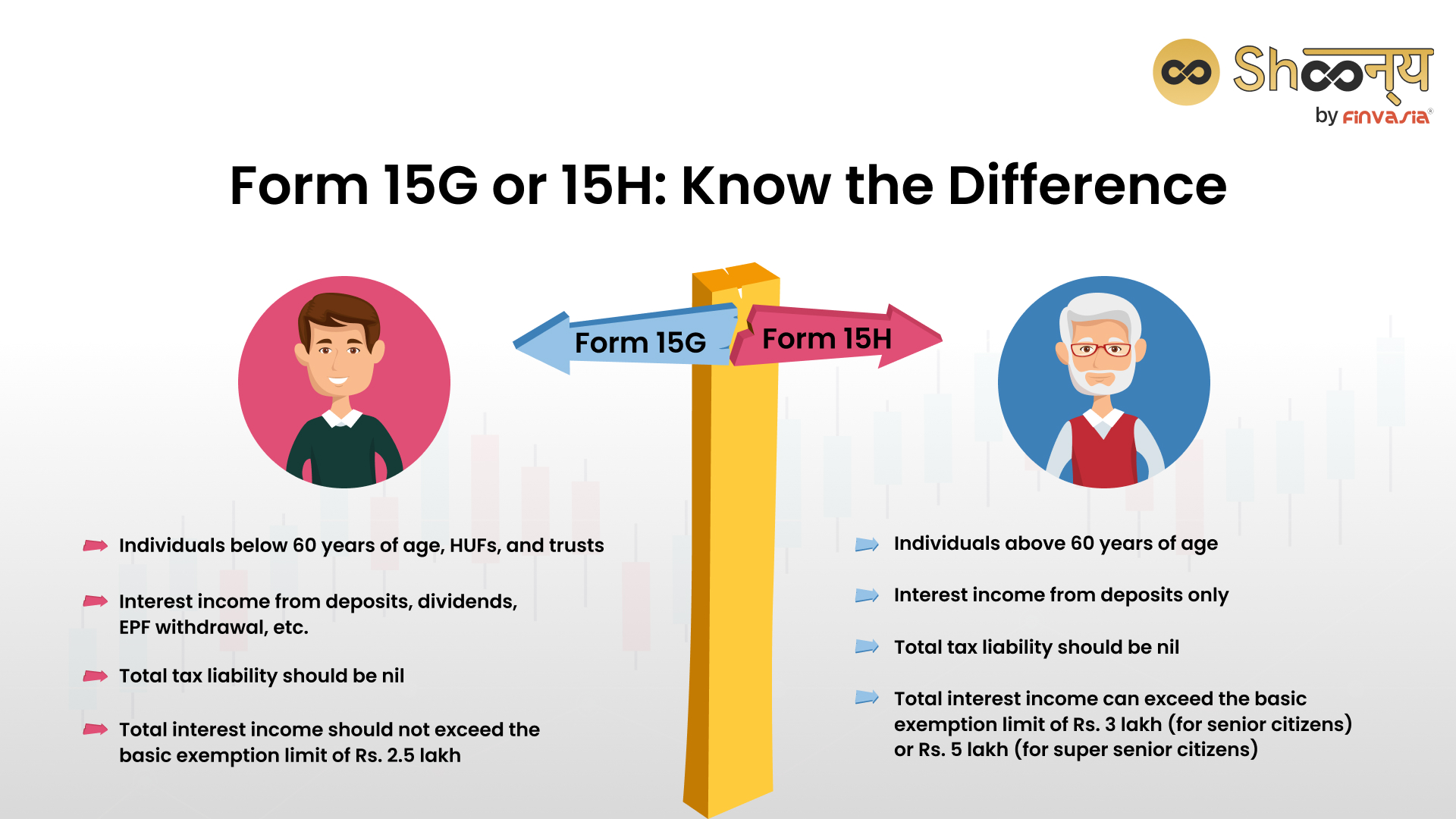
Form 15G is a crucial document that allows individuals and Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs) under 60 years of age to avoid Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) on their interest income. This benefit applies when their total income falls below the taxable limit.
What To Choose: Form 15G or Form 15H.
Forms 15 G and 15 H are self-declaration forms. It is designed to prevent unnecessary TDS deductions on income that is below the taxable threshold or the basic exemption limit. The basic exemption limit under the old regime applicable in case of a resident individual below the age of 60 years for the financial year 2023-24 is Rs 2.5 lakh, and for resident individuals aged 60 years or above but below 80 years, the exemption limit is Rs 3 lakh. For resident individuals aged 80 years or above, the exemption limit is Rs 5 lakh. For non-resident individuals, irrespective of the age of the individual, the exemption limit is Rs 2.5 lakh and for Hindu Undivided Family (HUF), the exemption limit is Rs 2.5 lakh. Under the new tax regime, the basic exemption limit is Rs 3 lakh for all age groups for FY 2023-24.
How to Properly Fill Out Form 15G or 15H
Form 15 G and 15 H are divided into two parts. Part 1 should be filled by the income recipient, while Part 2 is for the income payer. When you start filling out the form, it is crucial to provide all information accurately. Begin by filling in your personal details such as name, PAN, date of birth (DOB), residential address, email ID, and contact number. Ensure that the name and DOB you provide match the details on your PAN. Additionally, tick the appropriate box indicating your residential status. Remember, only resident individuals can benefit from Form 15G or H. Therefore, if you are a non-resident, there is no point in filing the form.
You are also required to mention the previous year (financial year) for which the declaration is being made. For example, if you are making the declaration for the current financial year, state the year as 2023-24. Clearly state the details of the income for which you are making the declaration. For instance, specify if it is interest from a post office deposit or rental income. You must also enter the total income from all sources that you have earned or will earn during the financial year.
Additionally, separately declare the income amount for which you seek TDS exemption through this specific form. For example, if your total annual income from all sources is Rs 2.4 lakh and you have earned an estimated income of Rs 5,000 from a post office FD, mention Rs 2.45 lakh as the ‘Estimated Total Income, including the estimated income earned on deposit(s)’. State Rs 5,000 separately in the space provided when submitting Form 15 to the post office.
Special Considerations for Interest Income
However, for individuals having interest income, the rules are a little different. “The condition of interest income exceeding the basic exemption limit pertains solely to Form 15G (those below 60 years) and does not apply to Form 15H (senior citizens). Form 15H can be submitted by senior citizens, even if their interest income surpasses the basic tax exemption threshold, provided their taxable income, after accounting for deductions, remains below the exemption limit.
How to Avoid Tax on FD Interest
The interest earned on fixed deposits (FDs) is fully taxable, but there are strategies to minimise or eliminate the tax burden. Explore options such as investing in tax-saving FDs, splitting FDs across banks, booking FDs in the name of family members, and submitting Form 15G/15H if your total income doesn’t warrant tax deductions.
Exploring Exemption Limit for TDS on FD Interest
The TDS exemption limit on FD interest varies depending on the individual’s age and the nature of the income source. For instance, TDS is to be deducted when the interest income earned exceeds Rs 40,000 and Rs 50,000 in a financial year for all resident assesses and resident senior citizens, respectively. In the case of interest from corporate bonds, the threshold for TDS is Rs 5,000.
For non-senior citizens, the TDS exemption limit on FD interest in India is Rs. 40,000 per financial year under section 194A of the Income Tax Act.
For senior citizens, this limit is higher, at Rs. 50,000. This means that if your total interest income from all FDs with a bank in a financial year stays below these limits, no TDS will be deducted.
TDS on FD Interest: Rates and Rules
The Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) rate on FD interest for non-senior citizens is 10%, applicable if the interest income exceeds Rs. 40,000 in a financial year under section 194A of the Income Tax Act. For senior citizens, this rate remains at 10%, but the threshold is higher at Rs. 50,000. However, if PAN details are not provided, TDS is deducted at a higher rate of 20%.
Form 15G vs 15H: Tailoring TDS Exemptions to Your Age
Forms 15G and 15H are powerful tools to dodge TDS on interest income from various sources. The key distinction lies in the age group: Form 15G applies to those below 60, while Form 15H is for senior citizens aged 60 or above. Importantly, Form 15H has no condition regarding interest income exceeding the basic exemption limit of Rs. 2.5 lakh, offering more flexibility to senior citizens.
You can download Form 15G and Form 15H from the websites of the Income Tax Department
Conclusion: Empowering Your Tax Knowledge
Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) can be complex, but with the right strategies and forms like 15G and 15H, you can navigate the world of taxation more effectively. By understanding the rent TDS limit and FD interest, you can minimise your tax burden and keep more of your hard-earned money in your pocket. Make informed choices, explore your options, and ensure your financial well-being.
If you have any questions or need further assistance, consult with a tax advisor to make the most of these tax-saving opportunities.
FAQs| TDS on FD
The new TDS rule on FD is that the bank will deduct TDS at the rate of 10% on the interest income from fixed deposits if it exceeds Rs 40,000 in a financial year for non-senior citizens and Rs 50,000 for senior citizens. This rule is applicable from April 1, 2023.
There is no tax-free amount for FD as such, but you can claim a deduction of up to Rs 1.5 lakh in a financial year under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act for investments made in tax-saving fixed deposits.
You can avoid Tax on FD interest by submitting Form 15G or 15H to the bank if your income is below the taxable limit. These are self-declaration forms that certify that your income is below the exempted threshold and you are not liable to pay any tax.
The TDS rate for interest income is 10% if the interest amount from all sources is more than Rs 40,000 (or Rs 50,000 for senior citizens). However, if the PAN of the recipient is not available, the TDS rate will be 20%.
The TDS rate for rent is 5% if the rent amount exceeds Rs 50,000 per month or part of a month. This rule applies to individuals and HUFs who are not liable for tax audits. The TDS should be deducted at the time of payment or credit of rent, whichever is earlier.
Yes, rent exceeding Rs 50,000 per month or part of a month is subject to TDS under Section 194-IB of the Income Tax Act. The tenant has to deduct TDS at the rate of 5% on the rent paid or credited to the landlord.
The TDS rate for Section 194-IA is 1% on the consideration for the transfer of any immovable property other than agricultural land. The TDS should be deducted if the consideration exceeds Rs 50 lakh. For the Section 194-IB, it’s 5% of the rent paid for any land or building or both. The TDS should be deducted if the rent exceeds Rs 50,000 per month or part of a month.
You can avoid TDS deduction on FDs by utilising Form 15G or 15H if your income falls below the taxable threshold, certifying non-taxability.
The new TDS rule on FD, effective from April 1, 2023, mandates a 10% deduction on FD interest exceeding Rs 40,000 for non-senior citizens and Rs 50,000 for senior citizens.
Source– www.moneycontrol.com
______________________________________________________________________________________
Disclaimer: Investments in the securities market are subject to market risks; read all the related documents carefully before investing.

