Beginner’s Guide To Bonds Investment in India
Investing in bonds allows individuals to diversify their portfolios while exploring the diverse investment opportunities of India’s financial market. With a range of options available, including government bonds, corporate bonds, and municipal bonds, investors can tailor their strategies to align with their risk tolerance and financial objectives. Bonds provide a steady stream of income through regular interest payments and the potential for capital appreciation.
In this blog, we will explore everything from types of bonds in India to the features of capital gain bonds and look at a suitable stock trading app for bond investment in India.
A bond is a type of debt security that allows investors to lend money to governments, municipalities, and corporations and receive interest payments and principal back at maturity. While bonds in the debt market may not offer the same potential for high returns as stocks, they can provide a stable source of income and diversification for an investment portfolio.
Difference Between Stocks and Bonds
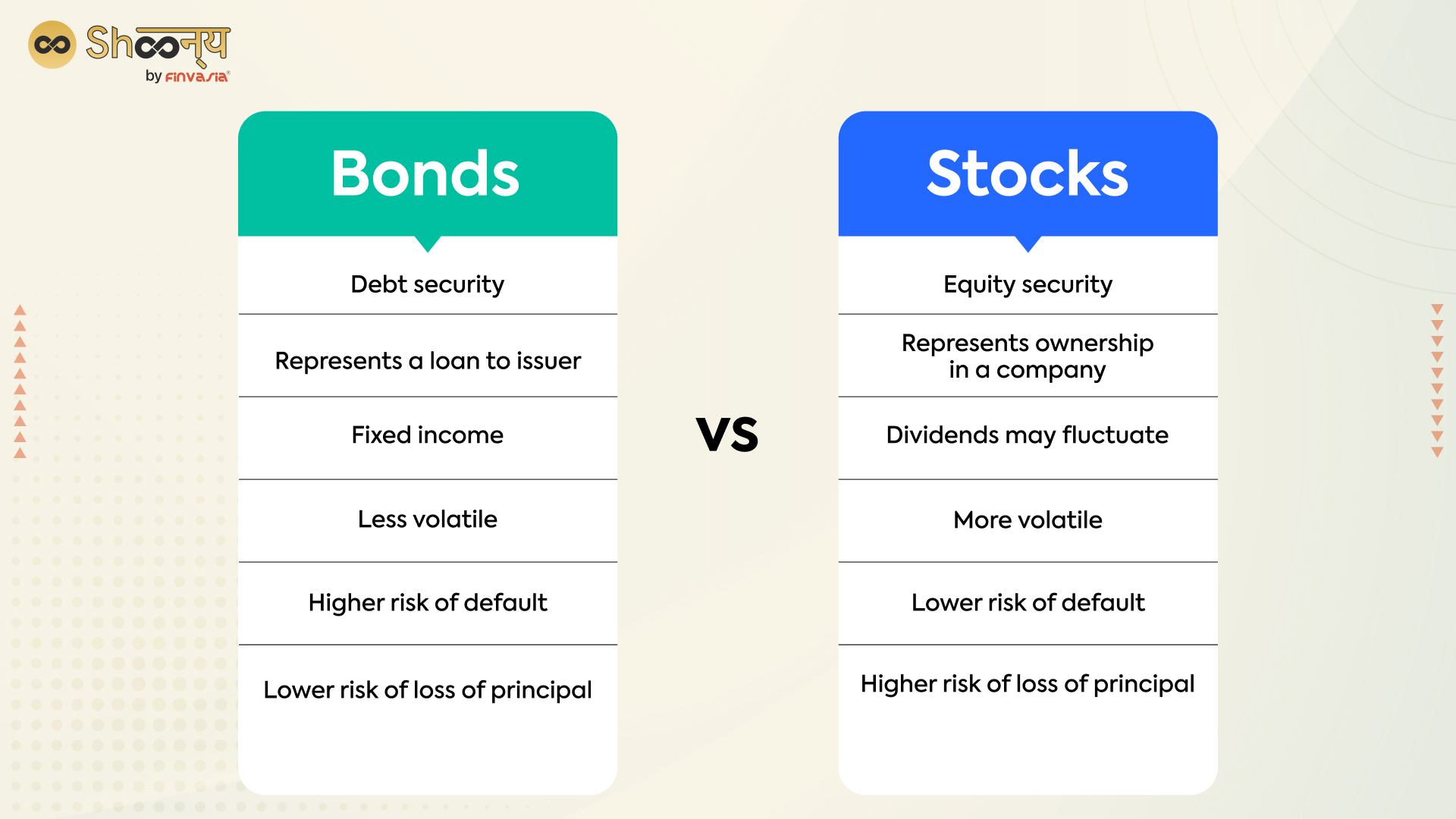
Bonds are debt securities that act as a loan to an issuer, while stocks represent an ownership stake in a company. When you purchase a bond, it means that you are lending money to the issuer in return for periodic interest payments and the return of principal at maturity.
When you buy a stock, you become a shareholder of the company, and thus, you are entitled to a portion of the company’s profits, as well as voting rights at shareholder meetings.
The value of bonds is typically less volatile than stocks, and the income from bonds is fixed, while the value and dividends of stocks can fluctuate. The risk of default is generally higher for bonds than stocks, but the risk of loss of principal is lower for bonds due to their fixed-income nature.
Bonds vs Stocks
To explore more about investing in bonds and their pricing, check- out how Bonds Work in Indian Market.
What are the Different Types of Bonds?
Various types of bonds can be traded in the share market. Here are a few examples:
- Corporate Bonds: These are issued by companies to raise capital for business operations, expansion, or acquisitions. Corporate bonds can be secured, meaning they are backed by collateral or unsecured.
- Government Bonds: Also known as sovereign bonds, national governments issue these to fund their operations and finance budget deficits. Government bonds are considered to be relatively low-risk due to the strong creditworthiness of most governments.
- Municipal Bonds: These are issued by cities, states, and other local government entities to finance public projects such as schools, roads, and infrastructure. Municipal bonds may be tax-free at the federal level and, in some cases, at the state and local levels as well.
- Tax-free Bonds: As the name suggests, these bonds offer tax-free interest income to investors. Governments or municipalities may issue them and may be subject to state and local taxes.
- Capital Gain Bonds: These bonds are issued by the government of India to finance infrastructure projects. Interest income from capital gain bonds is tax-free, and any capital gains upon the sale of the bonds are also tax-free.
Check- the types of Bonds in India to understand each in detail.
Out of all these, tax-free bonds and capital bonds are quite popular.
Exploring Debentures and Bonds in Detail.
Bonds and debentures are both types of debt securities that represent a loan to an issuer in return for periodic interest payments and the return of principal at maturity. The main difference between bonds and debentures is that bonds are typically backed by collateral, while debentures are unsecured. This means that in the event of default, bondholders have a claim on specific assets of the issuer, while debenture holders do not. As a result, debentures are generally considered to be higher risk than bonds and may offer higher interest rates to compensate for that risk. Both bonds and debentures can be traded in the share market and can be a source of income and diversification for an investment portfolio.
What are Debentures?
Debentures are typically unsecured, meaning they are not backed by collateral, and the issuer does not have a specific asset pledged as security for the loan. This makes debentures higher risk than bonds, which are typically secured by collateral. As a result, debentures may offer higher interest rates to compensate for the additional risk.
There are various types of debentures, including the following:
- Secured debentures: These debentures are backed by collateral, such as property or assets of the issuer. They generally carry lower risk than unsecured debentures.
- Unsecured debentures: These debentures are not backed by collateral and are considered to be higher risk than secured debentures.
- Convertible debentures: These debentures can be converted into a specified number of shares of the issuer’s stock at a predetermined price.
Non-convertible debentures (NCDs): These debentures cannot be converted into shares of the issuer’s stock and are considered to be purely debt-based investments.
Features of NCDs
Non-convertible debentures (NCDs) offer attractive features for investors:
- Higher interest rates compared to traditional fixed deposits.
- Potential for greater returns on investment.
- Various tenures are available to align with investment horizons.
- Regular interest payments provide a steady income stream.
- Diversification opportunities with different credit ratings and issuers.
- Tailor-made options based on risk appetite, income requirements, and financial goals.
- Provides a fixed-income investment avenue for individuals seeking stable returns.
- Offers a potential alternative to equity investments for conservative investors.
- It can be traded on exchanges, providing liquidity to investors.
- Suitable for both retail and institutional investors.
Check out the pros and cons of NCDs and Bonds
Exploring Tax-Free Bonds in India
Tax-free bonds are typically issued to raise capital for various public projects and initiatives, such as infrastructure development, schools, and hospitals. They offer a fixed and stable source of income to investors and may also offer the potential for capital appreciation if the bond price increases in the secondary market.
Investors who are looking to earn tax-free income or diversify their investment portfolio may consider adding tax-free bonds to their portfolios.
Eligibility in Tax-Free Bonds
- In India, tax-free bonds are typically available to resident individuals, Hindu undivided families (HUFs), trusts, and non-resident Indians (NRIs).
- Some tax-free bonds may have additional eligibility requirements, such as minimum investment amounts or income thresholds.
The Benefit of Tax-Free Bonds
- The main benefit of tax-free bonds is the tax-free nature of the interest income earned on the bonds.
- Tax-free bonds are an attractive investment option for those in high tax brackets or for those looking to reduce their overall tax liability.
If you are still confused about investing in tax-free bonds, check this out Why invest in tax-free bonds?
Capital Gain Bonds
investment in capital gain bonds, also known as 54EC bonds, is considered among the most effective methods to mitigate long-term capital gain taxes resulting from the sale of a capital asset. These bonds provide individuals with an opportunity to save on taxes by reinvesting their capital gains. Notably, the maximum investment limit for 54EC bonds is Rs. 50,00,000. By leveraging these bonds, investors can optimize their tax planning strategies while potentially earning returns on their investment, making it an appealing avenue for individuals seeking to safeguard their capital gains and enhance their financial outcomes.
Check out Key Things to Consider while Investing in 54EC Capital Gain Bonds.
Perks of Investing in Capital Gain Bonds
- Tax-free interest income: The interest earned on capital gain bonds is tax-free, which can make them an attractive investment option for those in high tax brackets.
- Tax-free capital gains: Any capital gains upon the sale of capital gain bonds are also tax-free, which can provide an additional source of tax-free income.
- Fixed and stable income: Capital gain bonds offer a fixed and stable source of income, as the interest rate and payment schedule are fixed at the time of issuance.
- Low risk: Capital gain bonds are issued by the government of India, which has a strong credit rating and a low risk of default. This makes capital gain bonds a relatively low-risk investment option.
- Potential for capital appreciation: If the price of the bond increases in the secondary market, investors may realise capital gains upon the sale of the bond.
Importance of Bond Ratings
The importance of bond ratings cannot be overstated when it comes to making wise and optimal investment decisions. Bond ratings play a crucial role in assessing the creditworthiness and default risk associated with bond issuers. Here’s why bond ratings hold significance:
- Risk Assessment: Bond ratings provide investors with a clear indication of the credit risk associated with a particular bond. Rating agencies evaluate factors such as financial stability, repayment ability, and market conditions to assign a rating. This helps investors gauge the likelihood of timely interest payments and the return of principal.
- Investment Decision Making: Bond ratings act as a valuable tool for investors in making sound investment choices. Investors can compare ratings across different bonds to assess their relative safety and potential returns. Higher-rated bonds generally offer lower yields but come with lower default risk, while lower-rated bonds may offer higher yields but carry increased risk.
- Portfolio Diversification: Bond ratings facilitate portfolio diversification by allowing investors to allocate their investments across bonds with varying risk profiles. A well-diversified portfolio balances higher-rated bonds for stability and lower-rated bonds for potentially higher returns, thus managing overall risk exposure.
- Investor Protection: Bond ratings offer a level of investor protection by providing transparency and accountability. Investors rely on rating agencies to independently assess the creditworthiness of bond issuers, helping them make informed decisions and avoid potential pitfalls.
If you are planning to make an investment in bonds in India, don’t forget to check How to Analyse the Credit Quality of a Bond Using Financial Ratios?
How Can You Make Bonds Investment in India?
To make bond investments in India, you can start by exploring the stock trading apps that offer online stock trading capabilities. These apps provide a convenient and user-friendly platform to buy and sell bonds. Research the available options, compare features, and choose an app that aligns with your investment goals.
With the right stock trading app, such as Shoonya, an online multi-asset trading platform that offers access to advanced financial tools and brokerage free trading. You can easily navigate the bond market, and access various bond options, to optimise your bond portfolio.
Key Takeaways
- Bonds provide an opportunity to diversify investment portfolios and explore India’s financial market.
- Types of bonds in India include government, corporate, municipal, tax-free, and capital gain bonds.
- Bonds offer a steady income stream through interest payments and potential capital appreciation.
- Bond ratings play a crucial role in assessing creditworthiness and default risk.
- Non-convertible debentures (NCDs) offer attractive features like higher interest rates and diversification options.
- Tax-free bonds provide tax-free interest income and are ideal for high-tax bracket individuals.
- Capital gain bonds help investors save on long-term capital gain taxes while potentially earning returns.
- Understanding bond ratings is essential for making informed investment decisions.
FAQs
Government bonds in India are considered secure investments. You can invest in them through brokers or bond dealers who are registered with SEBI and RBI. You’ll need a Demat account for government bond crediting. Additionally, mutual funds or ETFs offer an indirect way to invest in government bonds.
The minimum and maximum investment limits for bonds in India depend on the specific type of bond and the issuer. It’s best to consult with brokers or bond dealers for guidance, as these limits can vary.
Investing in savings bonds in India offers several advantages, including low risk, fixed interest rates, tax benefits, and flexible investment options. Also, they are the safest investment options.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Disclaimer: Investments in the securities market are subject to market risks; read all the related documents carefully before investing.








