I want to learn everything about the Stock and Share Market.
How can I learn online share trading? How to start trading in the stock market? Can you describe the process of online share trading? What are some common investing mistakes that I should avoid?
HELP ME!!!
Do you have all such questions in mind?
We have everything that shall help you learn the ABC about stock and share, trade, and investments, and we assure you, you read it once, and there you are, all set to jump into trading and investments!
Understanding the Concept of the Stock Market and Share Market!
A stock market, also known as a share market, is a market where stocks of publicly traded companies are bought and sold. A stock represents ownership in a company, and the stock market allows people to buy and sell these stocks. The stock market is an important part of the economy, as it enables companies to raise capital by selling stocks to investors and allows investors to buy and sell stocks in companies they believe will be successful.
What is the difference between Stock and Share?
A stock and a share refer to the same thing: ownership in a company. When you own a stock, you own a share of the company. For example, if a company has 100 shares of stock and you own one of those shares, you own 1% of the company.
Stocks and shares are often used interchangeably to describe ownership in a company, but there are subtle differences between them. “Stock” is typically used to refer to the overall market or the market value of a company’s shares, while “share” is more often used to refer to a specific unit of ownership in a company. So, for example, you might say, “I own 100 shares of stock in XYZ Company,” or “The stock of XYZ Company has gone up in value.”
In summary, a stock is a type of security that represents ownership in a company, and a share is a unit of ownership in a company. Depending on the context, they can have slightly different meanings when referring to company ownership.
A stock represents ownership in a company. Owning stock gives you a small stake in a company. You have the right to vote at shareholder meetings and to receive dividends, which are payments made to shareholders based on the company’s profits.
How are the Values of the Stocks Determined?
The value of a stock is determined by the company’s performance and the overall state of the stock market.
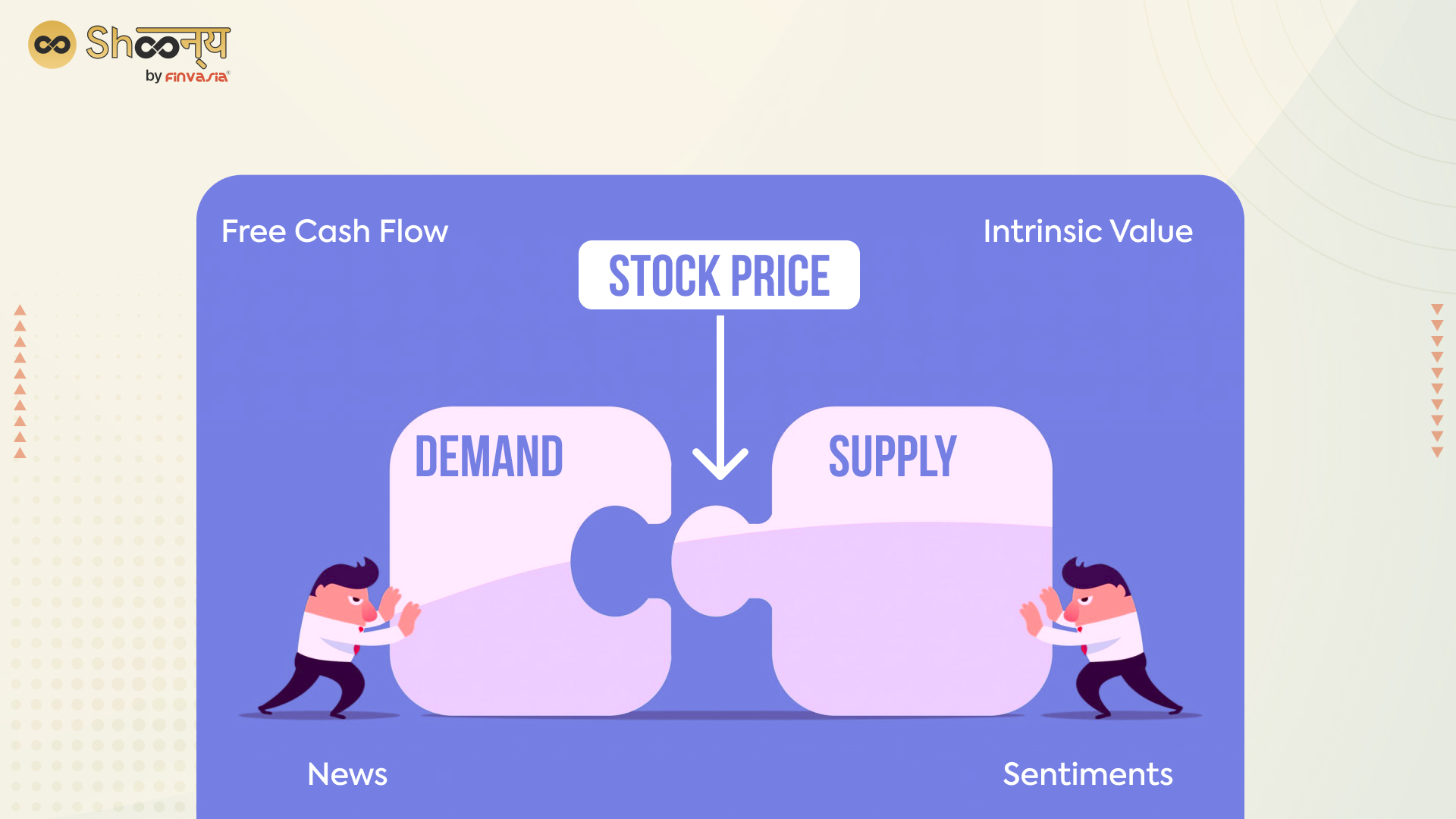
If the company is doing well and the stock market is strong, the value of the stock is likely to go up. If the company is performing poorly or the stock market is weak, the value of the stock is likely to go down.
In addition to stocks, other securities, such as bonds and derivatives, may also be traded on a stock market. In financial terms, a bond represents an investor’s loan to a borrower, such as a corporation or government. Derivatives derive their value from an underlying asset, such as a stock, commodity, or currency. Derivatives can be used to hedge risk or speculate on the underlying asset’s future movement.
Before discussing the Stock Market Basics, we know you would want to look at the 10 Key Terms to Know in the Share Market.
How does the Stock Market Work?

Stock market: This is a marketplace where stocks, or shares of ownership in a company, are bought and sold. The stock market is also known as the equity market.
When a company wants to raise capital, it can issue stocks and sell them to the public through an initial public offering (IPO). Once the stocks are listed on a public stock exchange, such as the NSE, they can be bought and sold by any individual.
Factors Affecting the Stock Prices.
Though, the price of a stock is determined by supply and demand. The price of a stock will increase if people are more interested in buying it than selling it. If more people want to sell a stock than buy it, the price will go down. Various factors, including the economy’s overall performance, individual companies’ performance, and investor sentiment, drive the stock market.
Investors can buy and sell stocks through a brokerage account (link this to which is the best Demat account with low brokerage charges), which is an account that allows them to trade securities. Brokerage accounts can be opened with a financial institution, such as a bank or brokerage firm , and investors can place orders to buy or sell stocks through the account. The brokerage firm will execute the trade on the stock exchange, and the investor’s account will be credited or debited based on the outcome of the trade.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Begin Investing
Here is a STEP BY STEP guide to begin investing in the market and enjoy your financial freedom.
Investing can help you build wealth and secure your financial future. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
- Determine your financial goals: The first step in investing is to determine what you want to achieve with your investments. For example, do you want to save for retirement, build wealth, or generate income? Knowing your financial goals will help you determine how much to invest and what types of investments are appropriate.
- Assess your financial situation: Take stock of your current situation by evaluating your income, expenses, and debts. This will help you determine how much you can afford to invest and what investments suit your risk tolerance and financial goals.
- Create a budget: Budgeting will help you stay on top of your expenses and ensure that you have enough money to invest. You might consider using an app or spreadsheet to track your income and expenses.
- Choose an investment account: There are several investment accounts to choose from, including individual retirement accounts (IRAs), employer-sponsored 401(k) plans, and brokerage accounts.
- Determine your asset allocation: Asset allocation refers to the mix of different types of investments in your portfolio, such as stocks, bonds, and cash. Your asset allocation should be based on your financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon.
- Choose your investments: Once you’ve determined your asset allocation, you can start selecting specific investments to include in your portfolio. Many types of investments exist, including stocks, bonds, mutual funds, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs). Consider seeking the advice of a financial advisor or doing your own research to select investments that align with your financial goals and risk tolerance.
- Monitor and review your portfolio: It’s important to regularly review your portfolio to ensure that it remains aligned with your financial goals and to make any necessary adjustments. Consider setting up automatic investments or rebalancing your portfolio to help you stay on track.
Investing can be a complex and intimidating process, but by educating yourself and developing a plan, you can set yourself up for success.
Types of Investments that you can choose from.
Now, let’s take a look at the different types of securities commonly traded in the financial markets.

1. Commodities and Commodity Trading
Commodities are physical goods that are traded on the market, such as agricultural products, metals, and energy products. Commodities can be traded through spot or future contracts.
What is Commodities Trading?
Commodity trading is the buying and selling of physical commodities in the spot or futures markets. But who handles the whole process? The Commodity Traders must be involved in the physical trading of the commodity, or they may trade financial instruments, such as futures contracts or options, that are based on the underlying commodity.
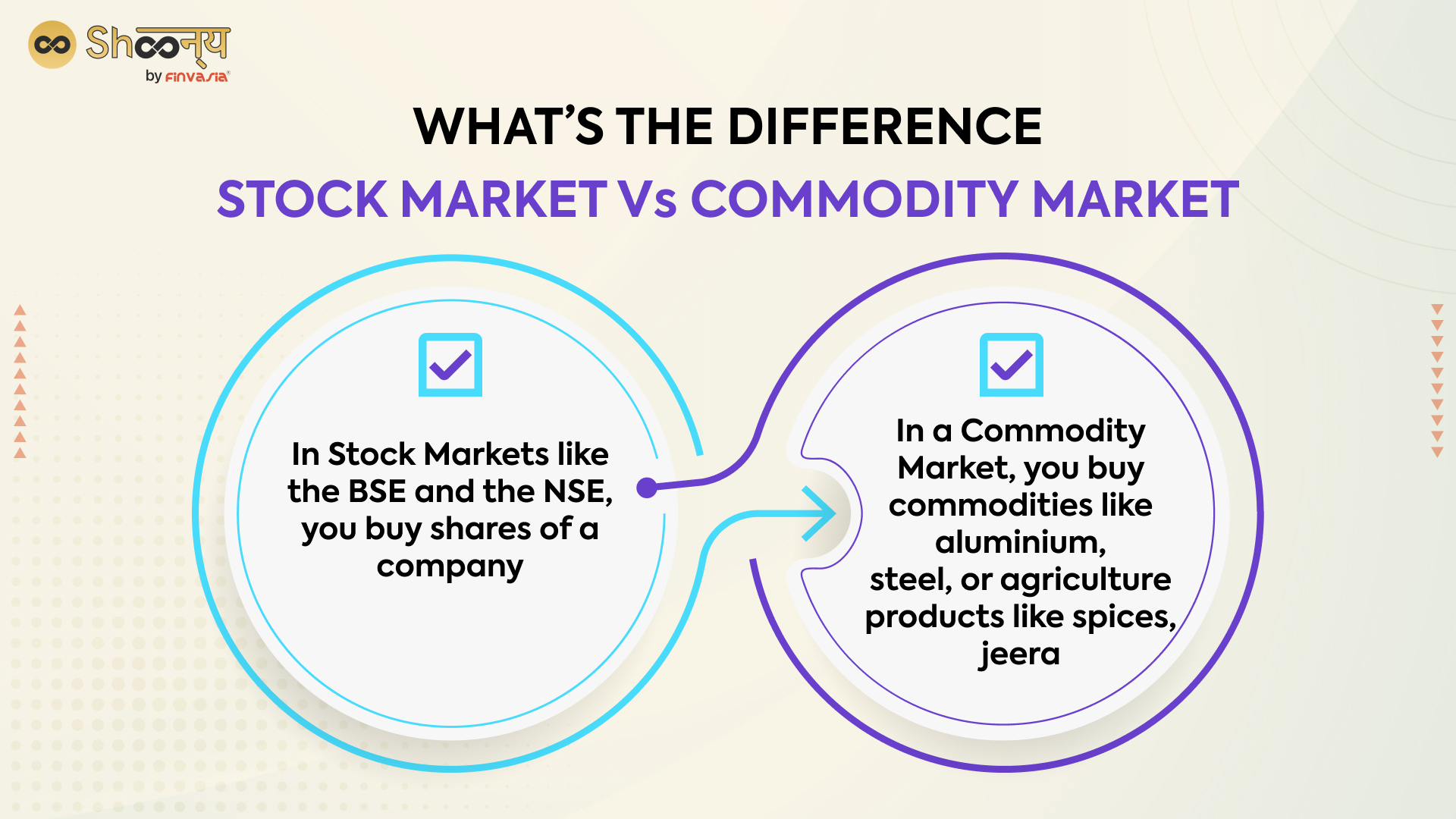
Is Commodity Trading better than Stocks?
Commodity trading can be a complex and potentially risky activity. It is important for traders to manage their risk carefully and to have a clear strategy for buying and selling commodities. It is impossible to say whether commodity trading is better or worse than stock trading, as it depends on an individual’s goals, risk tolerance, and market conditions. Both forms of trading involve risks, and it is important for traders to thoroughly understand the market and the factors that can impact prices before making any investment decisions.
2. Currency and Currency Market
Currency refers to money in a specific country. Forex, or foreign exchange, is the market where currencies are traded.
The currency market, also known as the foreign exchange (forex) market (What is Foreign Exchange – Your Complete Guide), is a decentralised global market for the trading of currencies. In the currency market, currencies are bought and sold based on their exchange rate, the price at which one currency can be exchanged for another.
The currency market is the largest financial market in the world, with an average daily trading volume of more than $5 trillion. It is open 24 hours a day, five days a week, and comprises a network of banks, dealers, and brokers.
In the currency market, traders and investors can buy and sell currencies in the form of currency pairs. A currency pair is a quotation of the relative value of one currency against another.
Factors affecting Currency Market
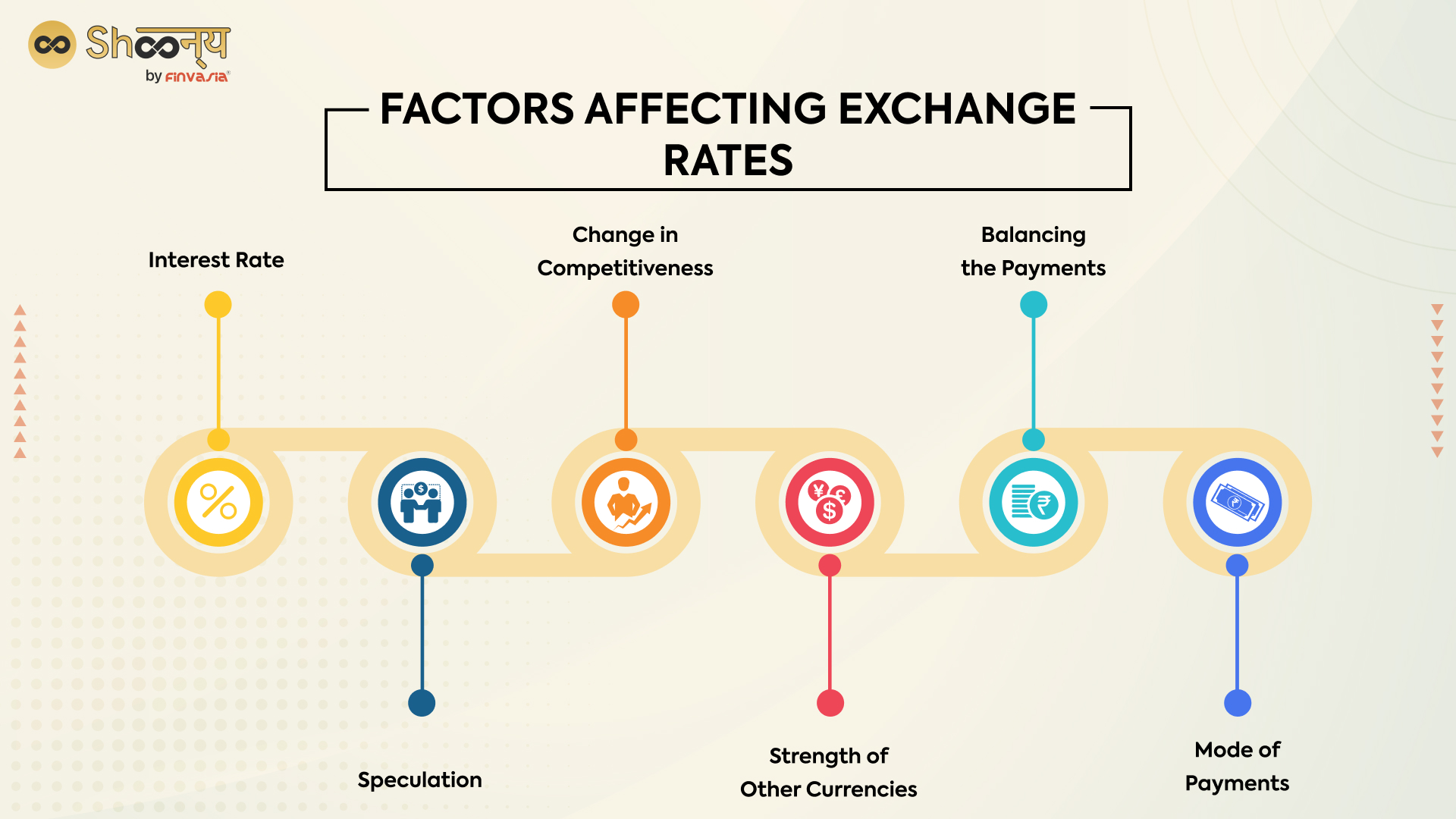
Currency markets are influenced by various factors, including economic indicators, politics, and central bank policies. These factors can affect the supply and demand for a particular currency, which can impact the currency’s exchange rate.
Traders and investors use the currency market to speculate on the movement of exchange rates and to hedge against currency risk. For example, a company that exports goods to a foreign country may hedge against currency risk by selling the foreign currency it expects to receive in the future in the currency market.
3. ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds)

These are investment funds that trade on an exchange, just like stocks. ETFs are typically made up of a basket of securities, such as stocks, bonds, or commodities.
Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) are investment vehicles that track the performance of a specific index or asset class. ETFs are traded on stock exchanges and can be bought and sold like stocks. As a result, they offer investors the ability to diversify their portfolios and access various asset classes in a single investment.
Types of ETFs
In India, ETFs have been available since 2001 and have become increasingly popular with investors. ETFs in India are regulated by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI). Several types of ETFs are available in India, including index-based ETFs, sector-specific ETFs, commodity ETFs, and gold ETFs.
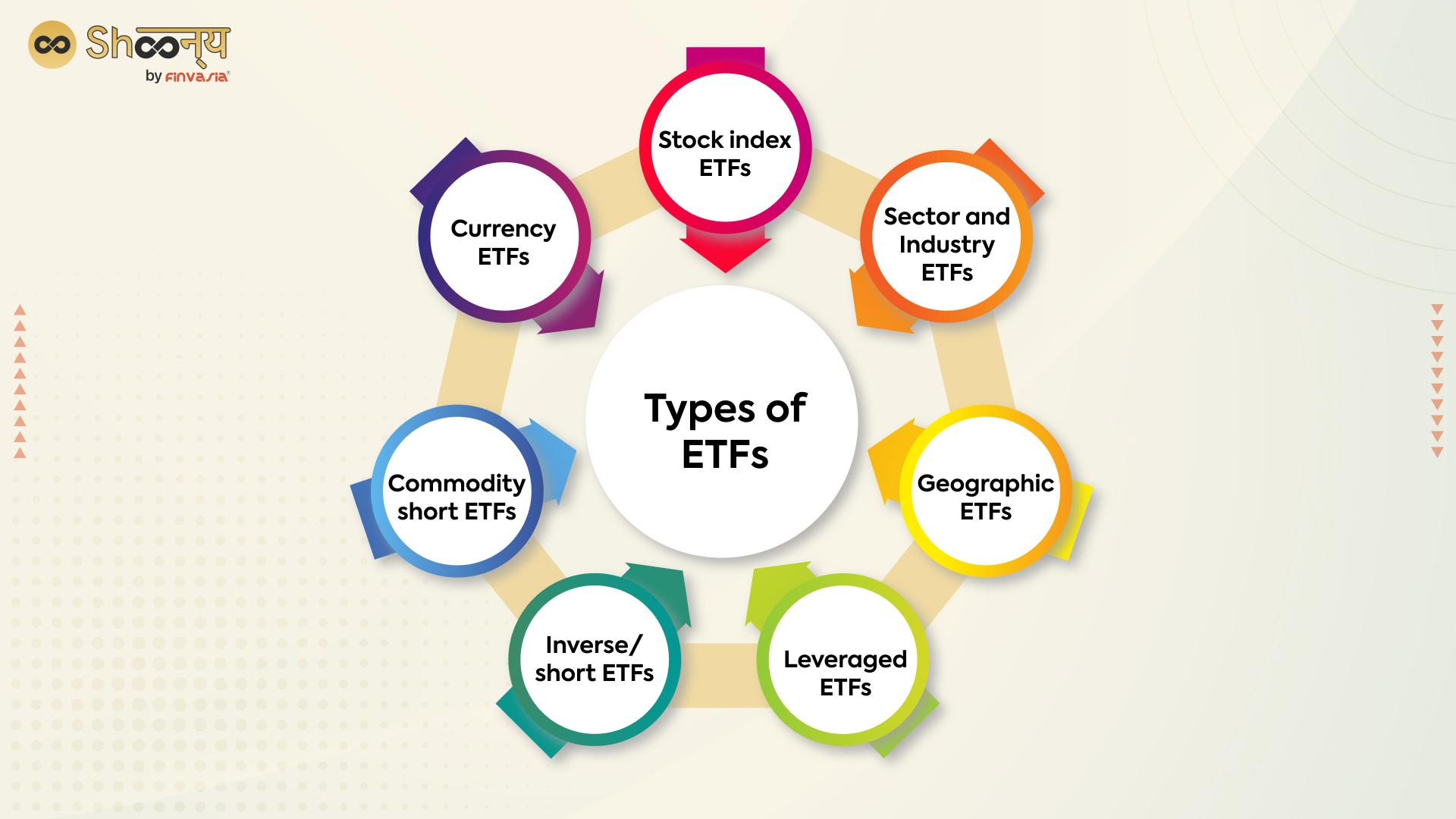
- Index-based ETFs track the performance of a specific index, such as the Nifty 50 or the BSE Sensex.
- Sector-specific ETFs invest in companies within a specific sector, such as technology or healthcare.
- Gold ETFs invest in physical gold or gold-related instruments, such as gold futures.
ETFs offer several benefits to investors, including low costs, diversification, and ease of trading. In this way, they can give investors exposure to a specific asset class or index without purchasing individual stocks or other securities. However, it’s important to note that ETFs carry their own set of risks, and investors need to understand these risks before.
4. Equity/Derivatives

Equity refers to ownership in a company, represented by shares of stock. Equity can be bought and sold on a stock exchange, such as the National Stock Exchange (NSE) of India or the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE).
Derivatives are financial instruments whose value is based on the value of an underlying asset, such as a stock, bond, commodity, or currency. Derivatives are used to hedge risk, speculate on price movements, or generate income. There are many types of derivatives, including futures, options, and swaps. Derivatives can be complex and involve a high level of risk, so it is important to understand how they work before investing in them.
In India, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) is the regulator responsible for overseeing the securities market, including the trading of equity and derivatives. SEBI sets rules and regulations to ensure smooth functioning and fair play.
5. NIFTY/SENSEX
The National Stock Exchange of India (NSE) is a leading stock exchange in India, and its Nifty 50 index measures the performance of 50 of the NSE’s largest and most active shares. The Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) is the oldest stock exchange in India, and the S&P BSE SENSEX (also known as the SENSEX) is an index of 30 of the largest and most representative stocks listed on the BSE.

The Nifty 50 and the SENSEX are both market capitalization-weighted indices, which means that the market value of the component stocks determines the level of the index. The index level reflects the stock market’s overall performance, with a rising index indicating an overall increase in stock prices and a falling index indicating a decline in stock prices.
Investors widely follow both the Nifty 50 and the SENSEX as benchmarks for the performance of the Indian stock market. They are both calculated and maintained by independent index providers, with the Nifty 50 being calculated by the National Stock Exchange of India and the SENSEX being calculated by the Bombay Stock Exchange.
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) is the regulatory authority responsible for overseeing the securities market in India, including the stock exchanges like the NSE and BSE. SEBI sets rules and regulations to ensure smooth functioning and provides oversight and supervision of the index calculation process to ensure the integrity of the indices.
6. Bonds
Bonds are debt securities that governments, municipalities, and corporations issue to raise capital. Buying bonds essentially means lending money to the issuer in exchange for interest payments and principal returns.
Bonds can be bought and sold on stock exchanges, such as the National Stock Exchange (NSE) of India and the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE). Indian securities market regulator Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) oversees the trading of bonds as well as the securities market in general.
There are different types of bonds, each with its unique characteristics.
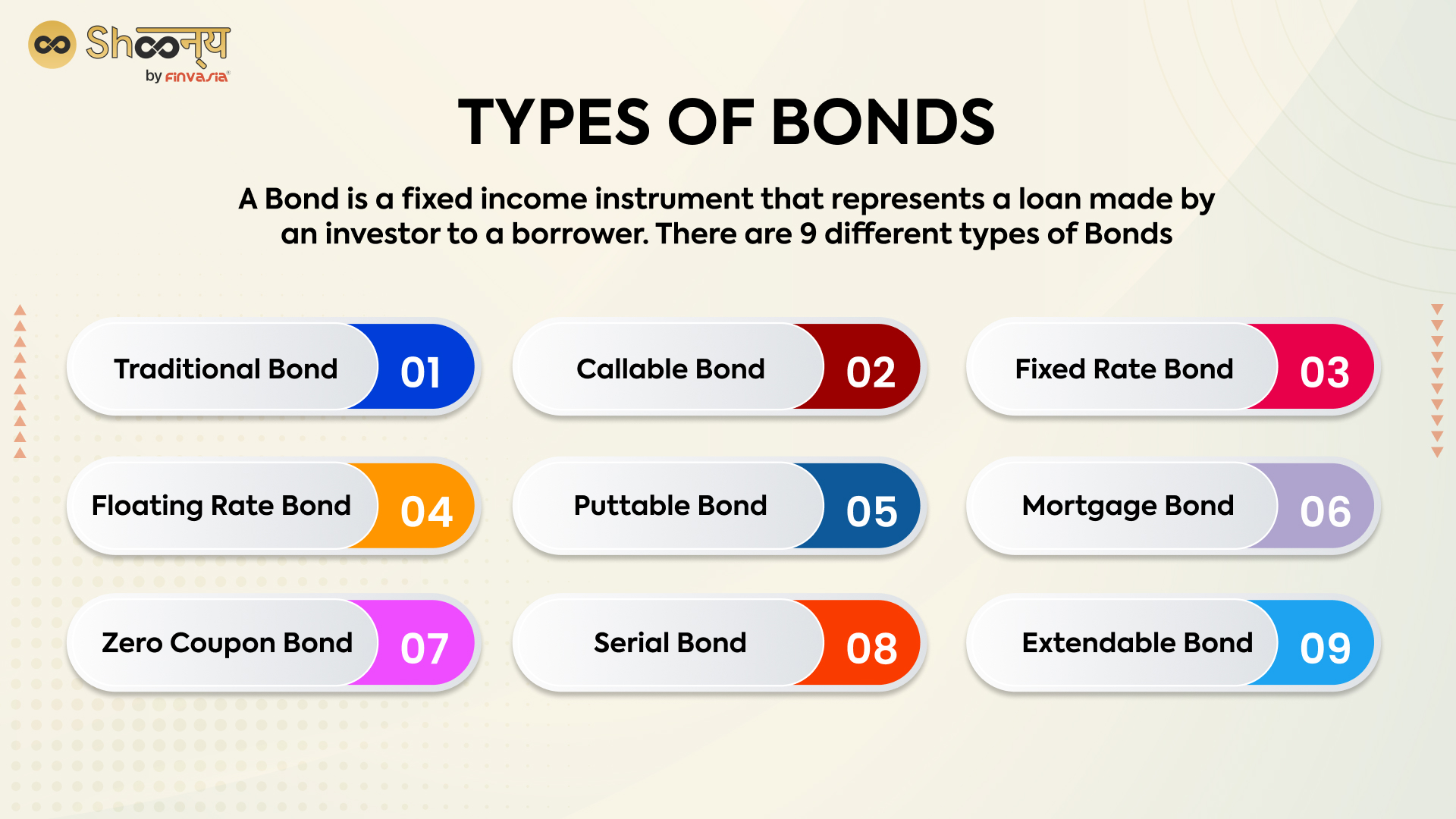
Some common types of bonds include government bonds, corporate bonds, municipal bonds, and mortgage-backed securities. The value of a bond can be affected by various factors, such as the creditworthiness of the issuer, the interest rate environment, and changes in economic conditions.
7. Futures
Futures are financial instruments that are used to manage risk or speculate on the future price movements of an underlying asset. A futures contract is an agreement to buy or sell a specific asset at a predetermined price at a specific time in the future. The underlying asset for a futures contract can be a commodity, such as gold or oil, or a financial instrument, such as a currency or a stock index. The asset’s price is agreed upon at the time the contract is signed, and the contract requires the buyer to purchase the asset and the seller to sell the asset at that price at the specified time in the future.
How are the Prices of Futures Determined?
Futures are traded on exchanges, such as the National Stock Exchange (NSE) of India or the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE)., and the price of a futures contract is determined by supply and demand.
If the underlying asset’s market price is higher than the price specified in the futures contract at the time the contract expires, the seller of the contract will make a profit. Conversely, the seller will incur a loss if the market price is lower than the price specified in the contract.
In order to be listed on a stock exchange and traded as futures, the underlying asset must meet certain requirements set by the exchange and be approved by the regulatory authority, such as the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
SEBI is responsible for regulating the trading and dealing of futures in the securities market in India. These regulations cover a wide range of issues, including listing requirements for future contracts, trading rules, and reporting and disclosure requirements.
8. Options
An option is a financial instrument that gives the holder the right, but not the obligation, to purchase or sell an underlying asset at a predetermined price at a future date. An option can be either a call option or a put option.
- A call option gives the holder the right to buy the underlying asset.
- A put option gives the holder the right to sell the underlying asset.
Options can be traded on a stock exchange, such as the National Stock Exchange (NSE) of India or the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE). To be listed on a stock exchange and traded as options, the underlying asset must meet certain requirements set by the exchange and be approved by the regulatory authority, such as the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
SEBI regulates the listing requirements for options contracts, trading rules, and reporting and disclosure requirements.
Why and How are Options Used?
Market participants can use options for a variety of purposes, including hedging against price movements in the underlying asset and speculating on the direction of price movements. However, options can be complex and involve a certain level of risk, so it is important to understand how they work before entering into an options contract.
9. Mutual funds
Mutual funds pool the funds of multiple investors and use them to buy a diversified portfolio of securities, such as stocks, bonds, and other assets. Investors are represented by professional fund managers who make investment decisions for the funds.
One of the main benefits of investing in mutual funds is that they offer the diversification, which means that the fund is invested in a broad range of securities and is less exposed to the risks associated with investing in a single security. This can make mutual funds a relatively low-risk investment option, especially for beginner investors who may not have much experience or knowledge about investing in the stock market.
Mutual funds can be bought and sold on a stock exchange, such as the National Stock Exchange (NSE) of India or the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE). However, to be listed on a stock exchange and traded as a mutual fund, the fund must meet certain requirements set by the exchange and be approved by the regulatory authority, such as the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
SEBI regulates the registration and licensing of mutual funds, disclosure and reporting requirements, and other operational and compliance issues.
10. IPO

An initial public offering (IPO) is when a privately-held company becomes a publicly-traded company by selling shares of its stock to the public for the first time. An IPO allows a company to raise capital by selling ownership stakes to a wide range of investors, including individual investors and institutional investors.
Investment banks manage the IPO process, which involves underwriting the offering, setting the terms of the offering, assisting the company with regulatory compliance and marketing the offering to potential investors. The shares are then listed on a stock exchange, such as the National Stock Exchange (NSE) of India or the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE), where they can be bought and sold by the public.
In India, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) is the regulatory authority responsible for overseeing the registration and licensing of IPOs, disclosure and reporting requirements, and other operational and compliance issues.
If you are interested in investing in an IPO,
There are several steps you can follow to invest in an initial public offering (IPO):

- Research the company: It is important to do your due diligence and research the company before deciding to invest in its IPO. This may include reviewing the company’s financial statements, business model, and competitive landscape.
- Open a brokerage account: In order to buy shares of a company’s stock, you will need to have a brokerage account.
- Place an order for IPO shares: When a company goes public through an IPO, it typically announces the details of the offering, including the number of shares being sold and the price range for the shares.
- Wait for the IPO to be allocated: After you place your order, you will need to wait for the IPO to be allocated.
- Buy the allocated shares: Once the IPO is allocated, your brokerage firm will inform you of the number of shares you have been allocated and the price at which you can buy them. You will need to have sufficient funds in your brokerage account to cover the purchase price of the shares.
DEMAT- What is it, and Why do I need it?

A DEMAT (short for “dematerialised”) account is an electronic account that is used to hold and manage securities in a paperless format. A DEMAT account is similar to a traditional brokerage account, but instead of holding physical certificates, it holds securities in electronic form.
The DEMAT system was introduced in India to streamline buying and selling securities and reduce the risk of fraud and errors. The DEMAT system allows securities to be bought and sold electronically without needing physical certificates. This can make the trading process faster and more convenient and reduce the risk of loss or damage to physical certificates.
The DEMAT system is widely used in the stock market and for other investments, such as mutual funds and government securities.
If you want to buy or sell securities through the DEMAT system, you must open a DEMAT account and follow the procedures for buying and selling securities through DEMAT.
Information about the DEMAT system and the regulatory environment for the DEMAT system in India is on the official website of the National Securities Depository Limited (NSDL).
What is Portfolio Management?

Portfolio management refers to the process of managing a group of investments to maximise returns and minimise risk. Portfolio management can be done by individual investors or by professional portfolio managers, who are responsible for making investment decisions on behalf of their clients.
In India, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) is the regulatory authority responsible for governing the securities market, including portfolio management. SEBI sets rules and regulations for portfolio managers and other market participants to ensure the market’s smooth functioning and fair play.
SEBI has specific rules and regulations for portfolio managers in India, which are outlined in the SEBI (Portfolio Managers) Regulations, 1993. These regulations cover various issues, including registration and licensing requirements for portfolio managers, disclosure and reporting requirements, and other operational and compliance issues.
Beginners need to understand the different types of securities and the risks and rewards associated with each one. It is also important to have a clear investment strategy to diversify your portfolio to manage risk; thus, you should learn about the Advantages and Disadvantages of Portfolio Management Services.
Why do I Keep Hearing About Personal Finance?
Personal finance is the process of managing your financial resources, including your income, expenses, savings, and investments. It involves making informed decisions about how to best use your financial resources to achieve your financial goals, such as building wealth, saving for retirement, or paying off debt.
How can personal finance help you?– Personal finance is important for a number of reasons. First, it helps you to understand your financial situation and to make informed decisions about how to manage your money. This can help you to avoid financial pitfalls, such as overspending or making poor investment decisions.
Before actually working on your finances, you must know certain basic principles of Personal Finance to effectively manage your money. Following this comes overall Personal finance management, the process of overseeing and organising your financial resources to achieve your financial goals. This may include setting financial goals, creating a budget, saving and investing, and managing debt.
- Set financial goals: It is important to have a clear understanding of your financial goals and to set specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals.
- Create a budget: Creating a budget can help you to track your spending and to identify areas where you can save money. It is important to regularly review and update your budget to ensure that it reflects your current financial situation and goals.
- Save and invest: Building a financial cushion by saving money is important for financial security and independence. It can also help you to achieve your financial goals, such as buying a home or saving for retirement.
- Manage debt: Debt can be a useful financial tool, but it is important to manage it responsibly. This may include paying off high-interest debt, such as credit card balances, as quickly as possible and avoiding taking on more debt than you can reasonably handle.
With Personal Finance comes another aspect, i.e., Financial planning, the process of creating a plan to achieve your financial goals. It involves analysing your current financial situation, setting financial goals, and developing a plan to achieve those goals through effectively managing your financial resources.
There are many ways to manage your personal finance, including investing in the stock market, trading in bonds and other securities, and investing in mutual funds. It is important to carefully consider your financial goals and risk tolerance before making any investment decisions.
Market Trends- Are they Important?
Market trends refer to the direction in which the prices of securities or other assets are moving over a certain period. Market trends can be upward, downward, or sideways, and a variety of factors, including economic conditions, company performance, and investor sentiment, can influence them.
In the stock market, market trends can be studied by analysing the price movements of individual stocks or stock indices, such as the S&P 500 or the Nifty 50. In addition, some tools and techniques can be used to analyse market trends, such as charting, technical analysis, and fundamental analysis.
It is important to note that market trends are not always predictable, and they can change quickly. Therefore, it is important for investors to carefully consider the risks and potential rewards before making investment decisions based on market trends.
You can keep checking our market trends section to keep in touch with daily market updates. You can also use more than 100 technical indicators to analyse real-time price data and decide for yourself before buying or selling any asset or security.

